What is the history of African Violet variegation?
- African Violets are popular houseplants known for their showy flowers and attractive foliage. The variegation in African Violet leaves, or the appearance of white or yellow markings on the green leaves, is a naturally occurring genetic mutation that was first documented in the early 20th century.
- African Violets were first discovered in the tropical rainforests of Tanzania and Kenya in the late 19th century. They were later introduced to Europe and North America, where they quickly became popular as houseplants due to their beauty and ease of care.
- The first variegated African Violets were discovered in the wild, and their distinctive leaves immediately caught the attention of botanists and horticulturists.
- Over the years, African Violet breeders have worked to cultivate and stabilize variegated varieties, resulting in a wide range of cultivars with different patterns and colors of variegation. Today, African Violets with variegated leaves remain popular among plant enthusiasts and are widely available in garden centers and online.
- Few of my personal favorite variegated varieties are Shirls Hawaiian Lei, Precious Lavender, Definitely Darryl & Morgans Mediterranean Escape.
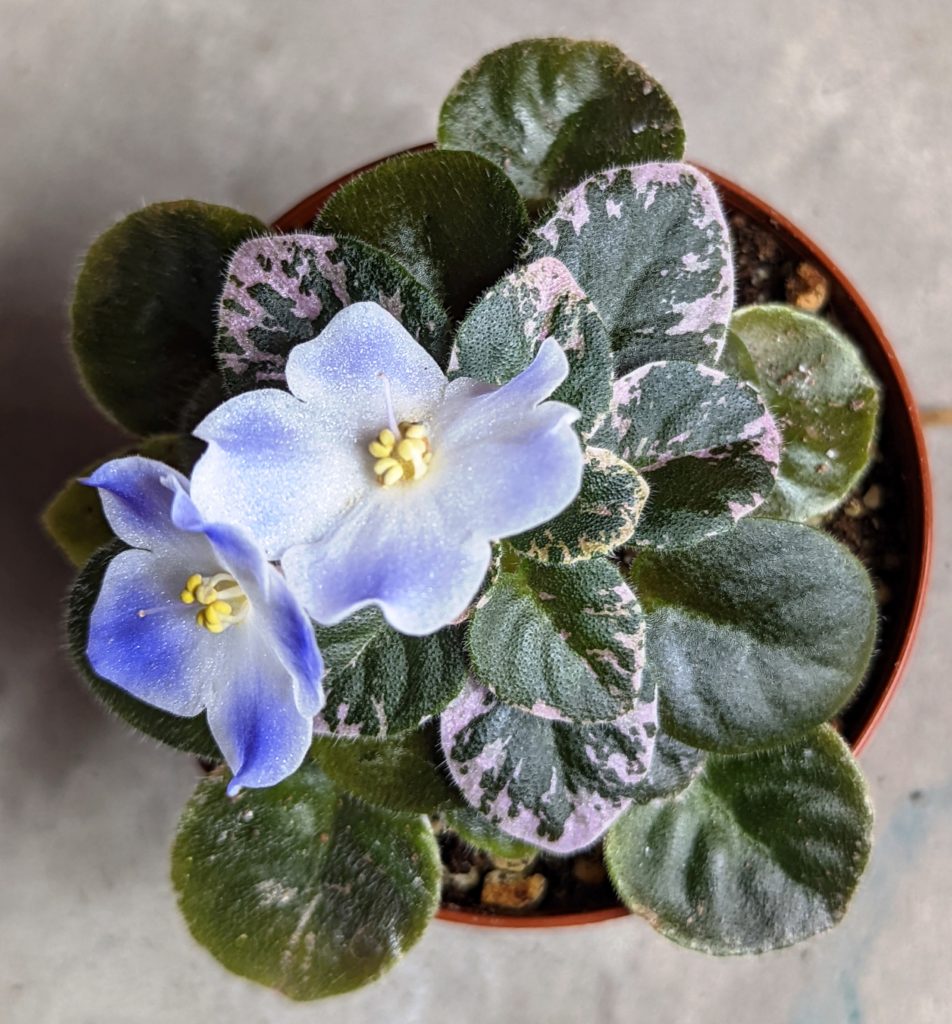
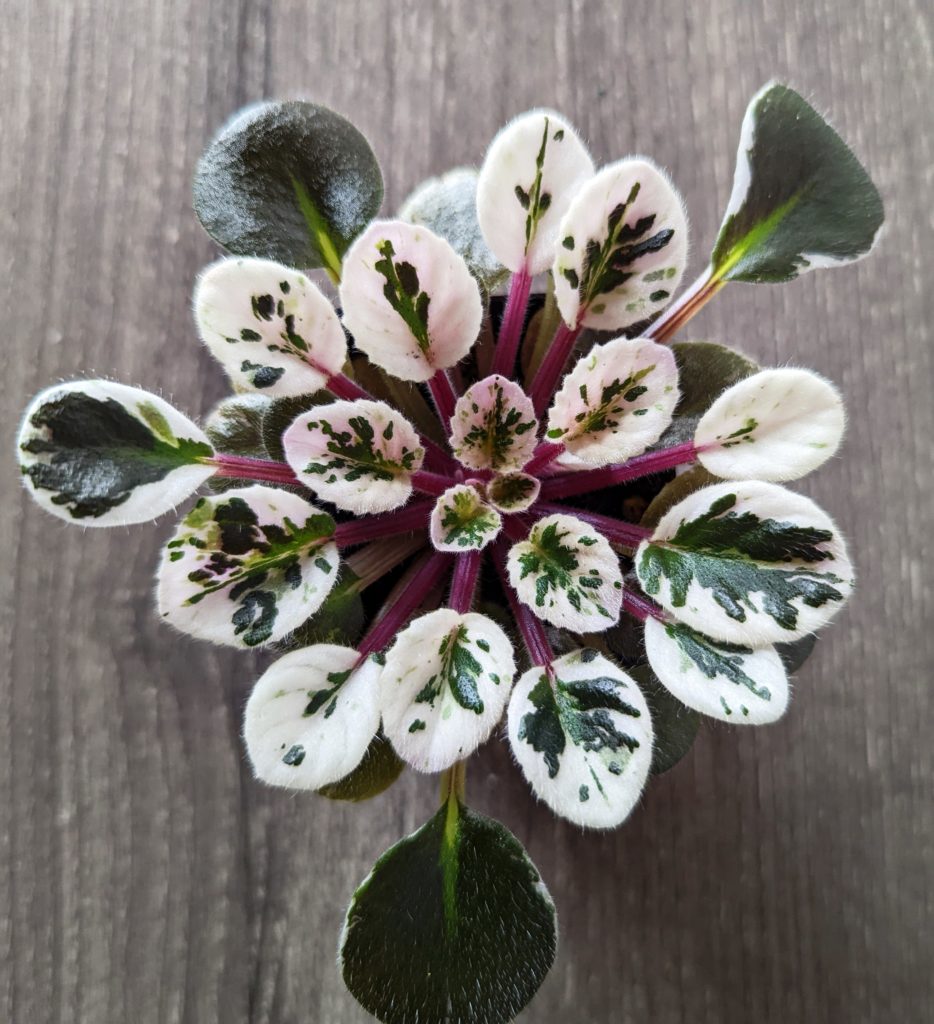
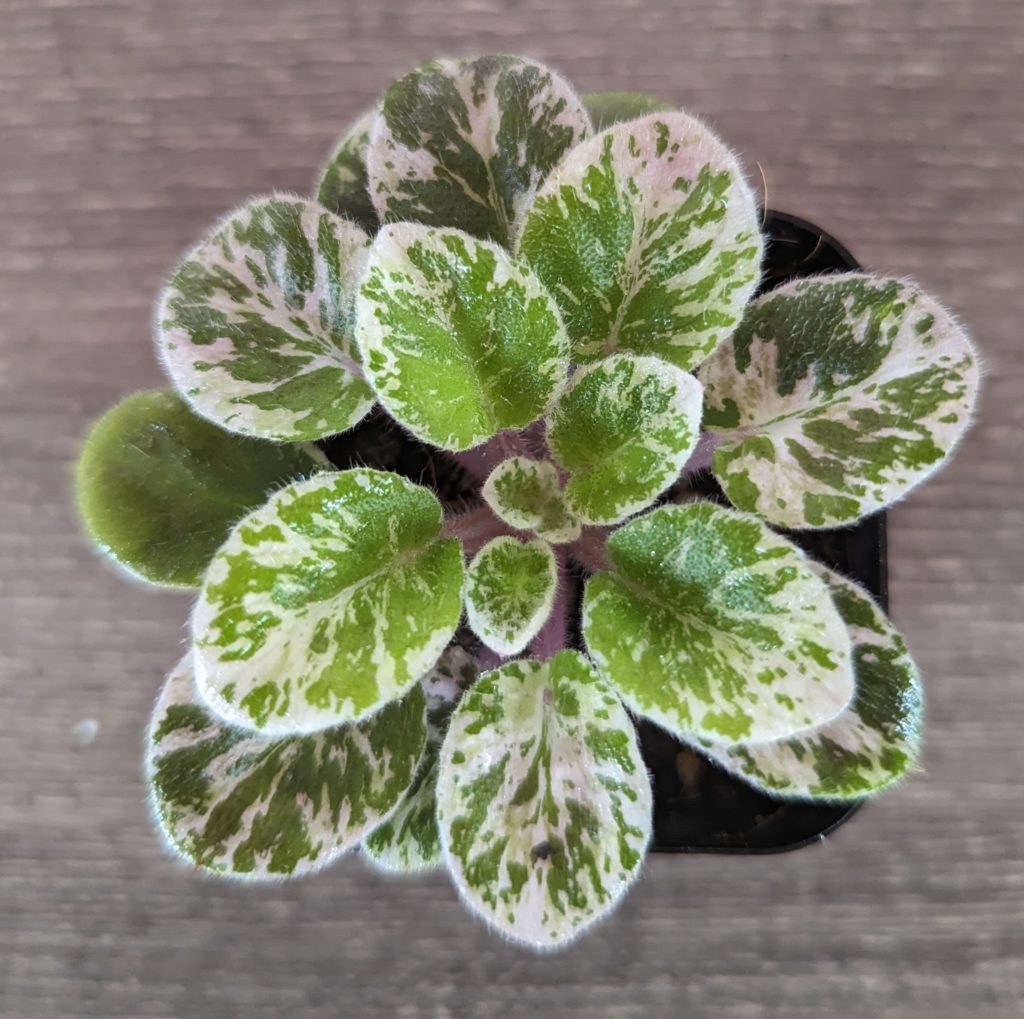
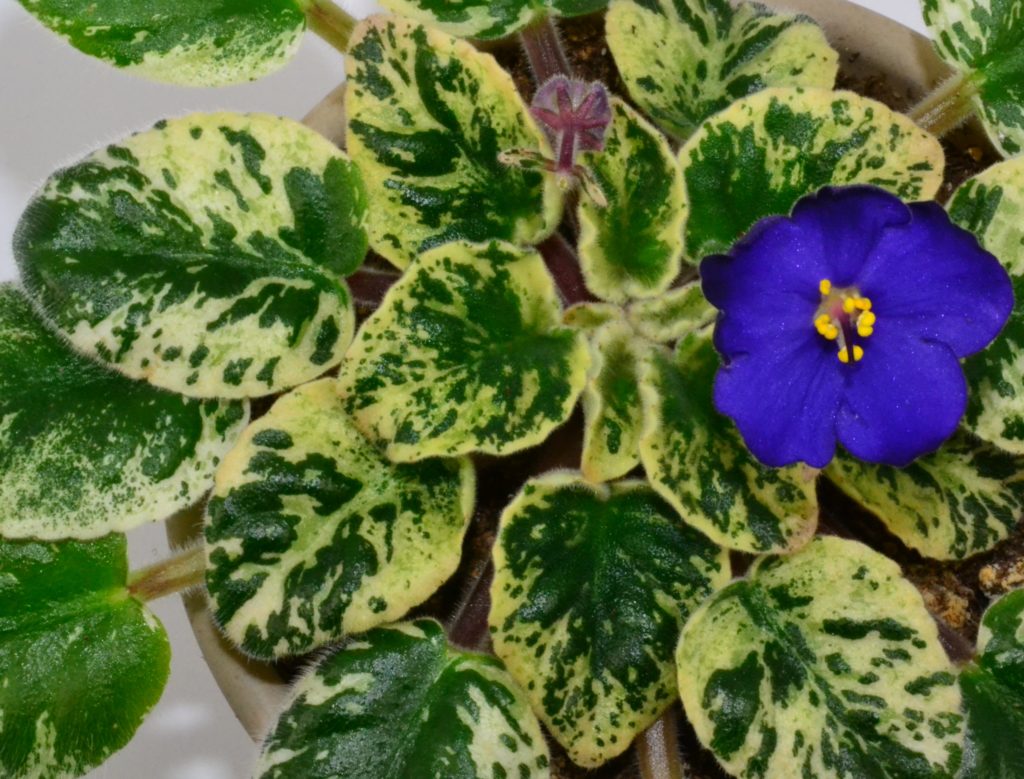




- The first known variegation in an African Violet appeared in 1957 when the American hybridizer, Mrs Tommie Louise Oden, propagated “White Pride” (a popular double white variety at the time) that mutated and produced variegated white margins on its leaves.
- While experimenting with this plant, she successfully propagated the variegated leaf trait through nine successive generations and this new variegated leaf variety was named “Tommie Lou” in her honor.
- Tommie Louise Oden was an African Violet hybridizer and enthusiast, who was known for her contributions to the African Violet community. She was a prominent figure in the African Violet Society of America and her work helped to advance the breeding and cultivation of these popular houseplants.
- Mrs. Oden is best known for her hybrids and cultivars of African Violets, which she bred for their unique colors, patterns, and shapes. Some of her most popular varieties have become widely recognized in the African Violet community and are highly sought after by collectors and enthusiasts.
- Although information on Mrs. Tommie Louise Oden is scarce, her legacy in the African Violet community continues to be remembered and honored by those who admire and grow these beautiful plants.
African Violet, perlite and coco coir shown below:
What is African Violet leaf variegation?
- Leaf variegation is a pattern of different colors on the leaves of an African Violet plant, where the coloration is not uniform, but rather consists of different shades of green, yellow, white, and other hues.
- This can be due to genetic mutations or other factors that cause chlorophyll to be produced unevenly in the African Violet leaf, resulting in the different colors.
- Leaf variegation can also be seen as an ornamental feature in African Violet plants.
How does African Violet leaf variegation happen?
African Violet leaf variegation can occur due to several reasons, including genetic mutations, virus infections, and other factors that affect chlorophyll production. Some of the most common causes are:
- Chimera: A genetic mutation where cells of different genotypes coexist within the same African Violet leaf, causing differences in coloration.
- Albinism: A condition where an African Violet plant lacks the ability to produce chlorophyll, leading to white or yellow variegation.
- Piebaldism: A phenomenon where chlorophyll production is limited or stopped in certain areas of the African Violet leaf, causing the variegation.
- Virus infections: Certain plant viruses can cause variegation in leaves as a side effect of the infection.
- Nutrient deficiencies: Lack of certain nutrients such as iron, magnesium, and others can also cause variegation in African Violet leaves.
It’s important to note that the specific cause of leaf variegation can vary among different plant species and cultivars, and that the underlying mechanisms can be complex.
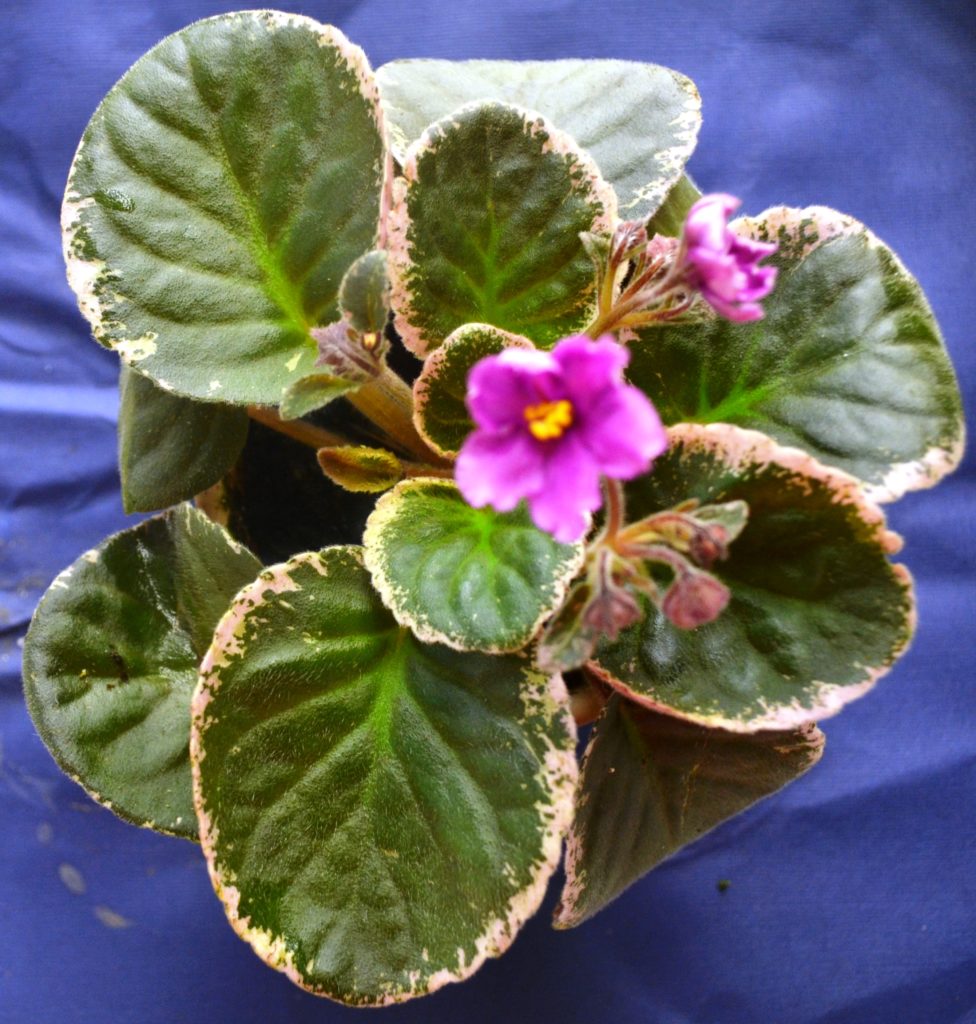
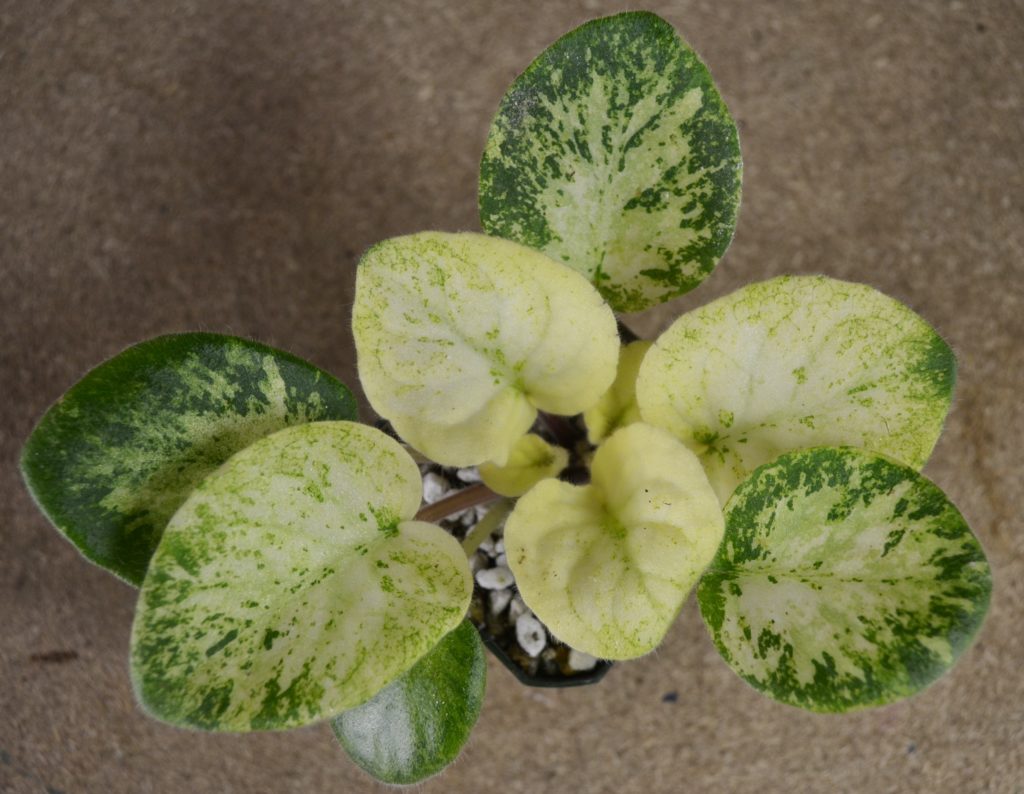
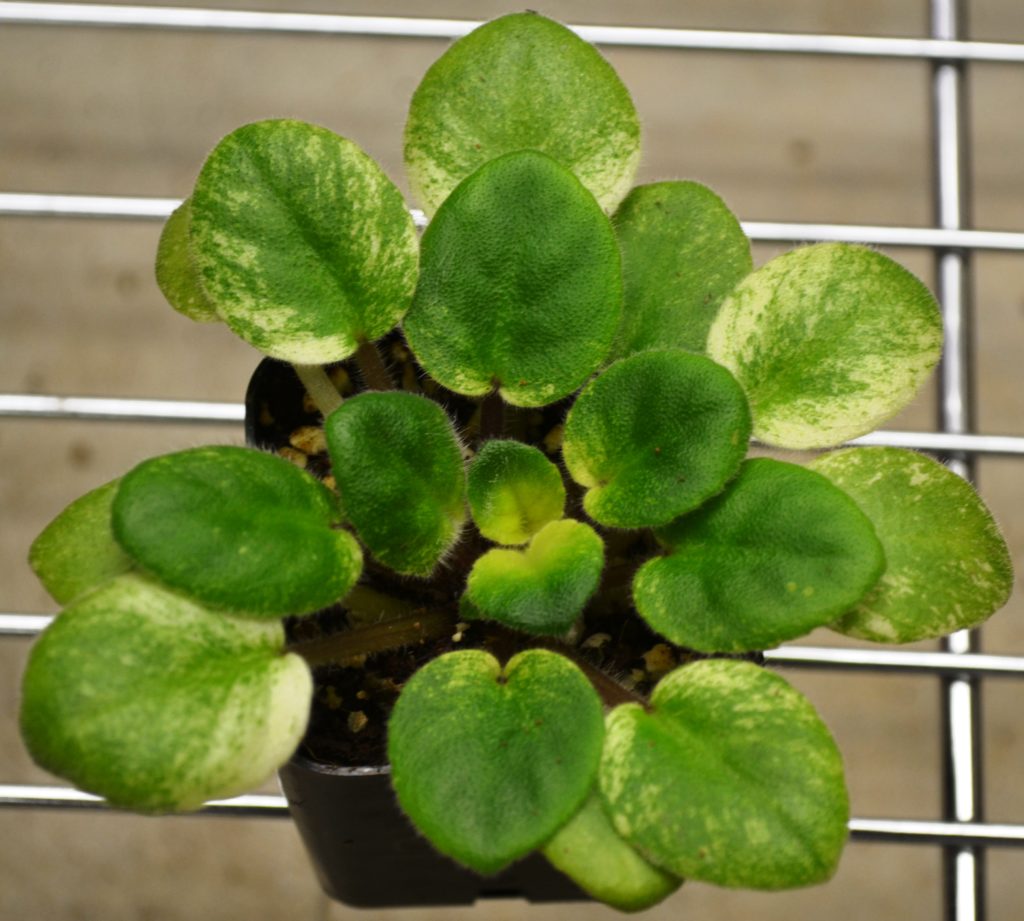
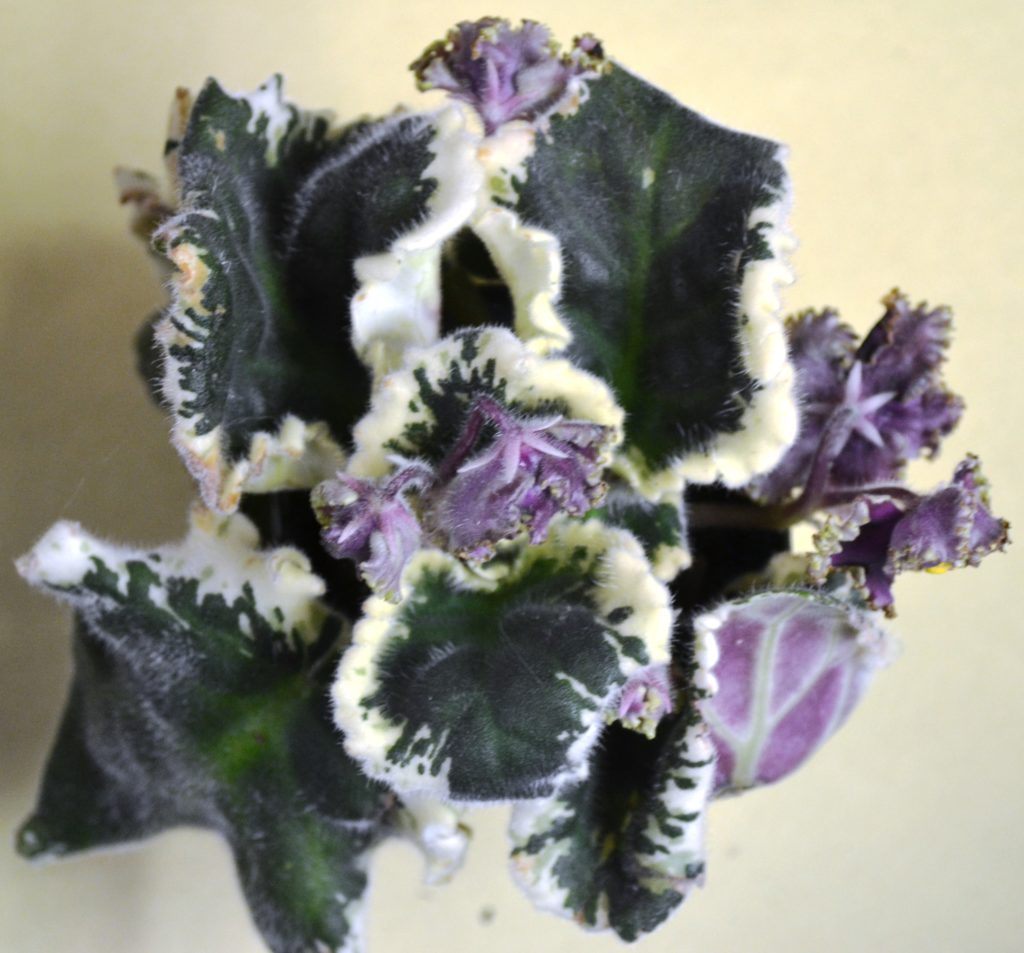




What is the science behind African Violet leaf variegation?
- African Violet leaf variegation is caused by disruptions in the normal production and distribution of chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for giving leaves their green color. Chlorophyll is produced in chloroplasts, which are organelles in the cells of leaves.
- There are several different mechanisms that can lead to African Violet leaf variegation, including genetic mutations, virus infections, and nutrient deficiencies. For example, in the case of a genetic mutation, cells within a leaf can have different genetic information, leading to differences in chlorophyll production. This can result in the coexistence of cells with normal chlorophyll production and cells with reduced or absent chlorophyll production within the same African Violet leaf, leading to the variegation pattern.
- In the case of virus infections, the virus can interfere with chlorophyll production in affected cells, leading to variegation. Nutrient deficiencies can also affect chlorophyll production and cause variegation. For example, a lack of iron can result in chlorosis, a yellowing of the African Violet leaves due to reduced chlorophyll production.
- It’s also worth noting that some African Violet plants have naturally occurring variegated leaves, as it can be a desirable trait for ornamental purposes. These cultivars can be propagated through cloning or other methods to maintain the variegated pattern.
Examples of 2″ & 3″plastic pots, great to keep a few extra in your growing tools:
What are the different types of leaf variegations in African Violets?
African violets (Saintpaulia) are a popular houseplant known for their delicate blooms and attractive leaves, which can exhibit a range of variegation patterns. The following are some of the different types of leaf variegations seen in African violets:
- Marginal variegation: This is a pattern where the edges of the leaves are a different color from the rest of the leaf, often white, yellow, or pink.
- Mosaic variegation: In this pattern, small patches of different colors are scattered across the leaf.
- Speckled variegation: In this pattern, small specks of different colors are dispersed evenly across the leaf.
- Veined variegation: This pattern is characterized by veins of a different color running through the leaf.
- Central variegation: This pattern is characterized by a center of a different color surrounded by the normal green of the leaf.
It’s worth noting that the specific type of variegation seen in African violets can vary greatly depending on the cultivar, and that many hybrids and cultivars have been developed for ornamental purposes to produce specific patterns and colors.
What is Tommie lou variegation in African Violets?
- Tommie Lou variegation is a specific type of leaf variegation pattern seen in African violets (Saintpaulia).
- This type of variegation is characterized by a white or yellow center surrounded by a dark green ring, creating a bull’s-eye pattern.
- The specific pattern can vary depending on the cultivar and can include different sizes and shapes of the white or yellow center.
- Tommie Lou variegation is a highly desirable ornamental feature in African violets, and many cultivars have been developed to produce this specific pattern.
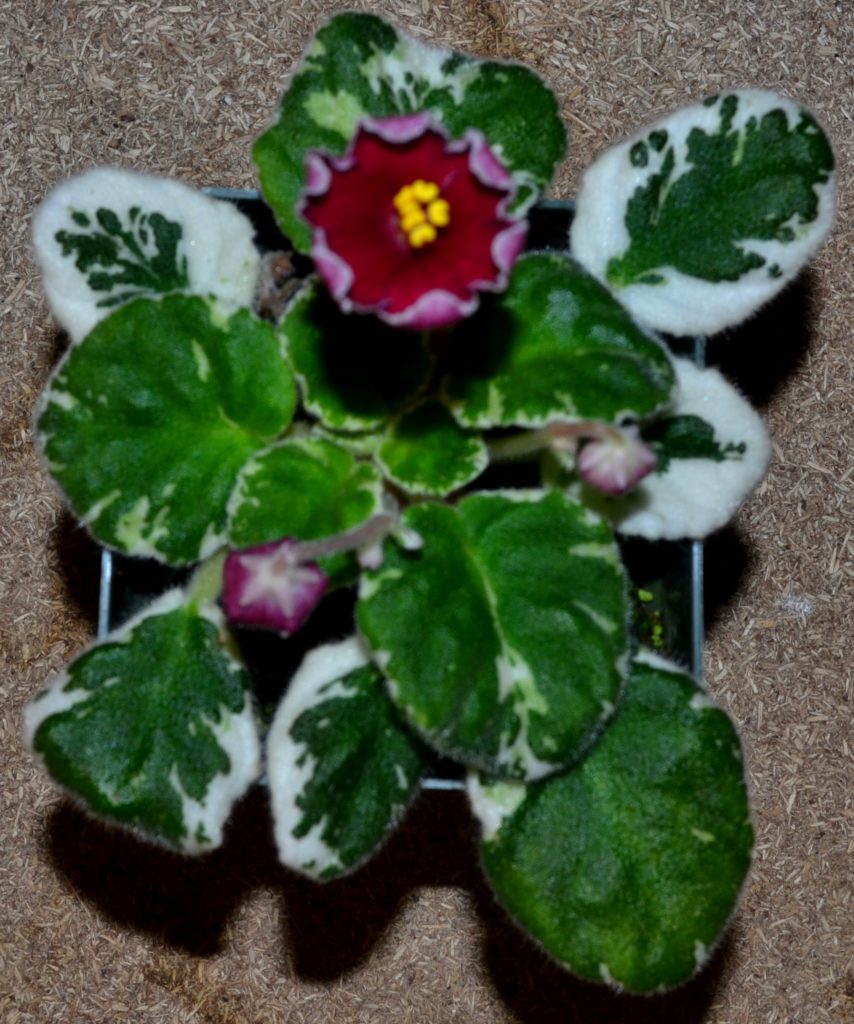
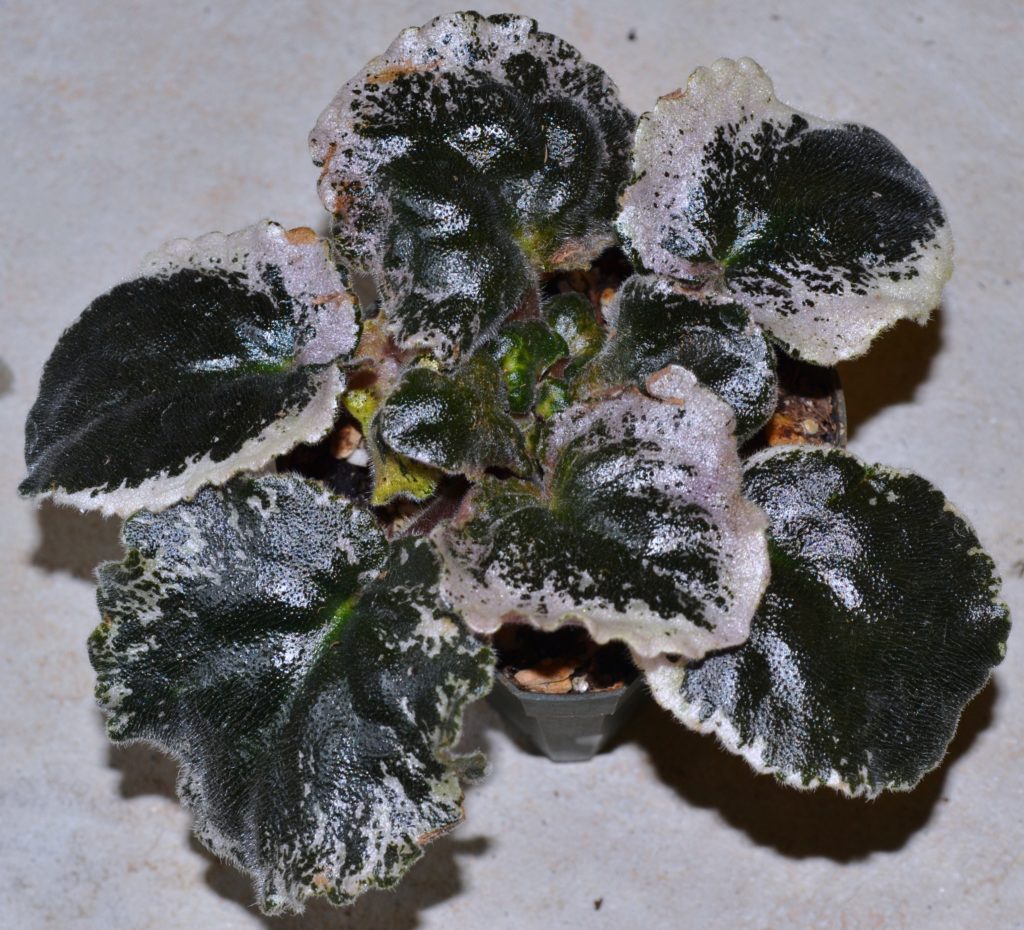
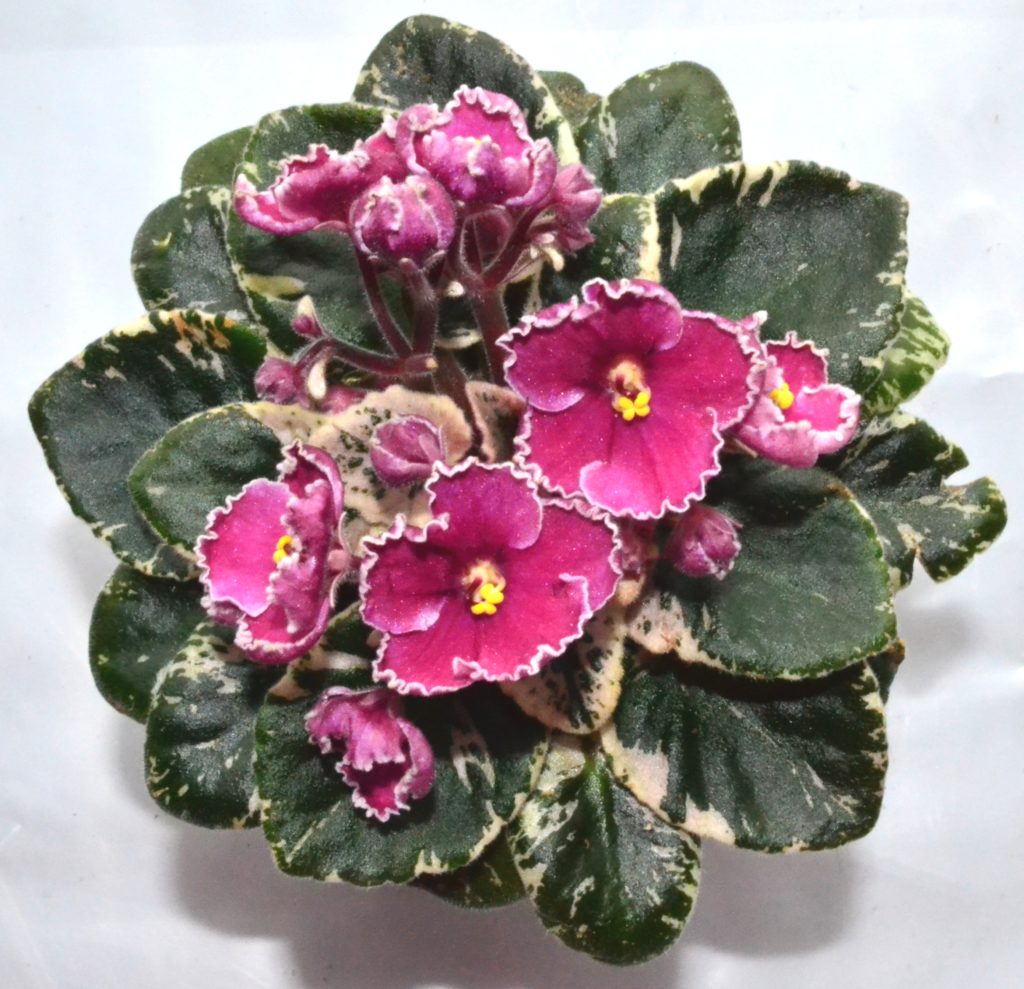
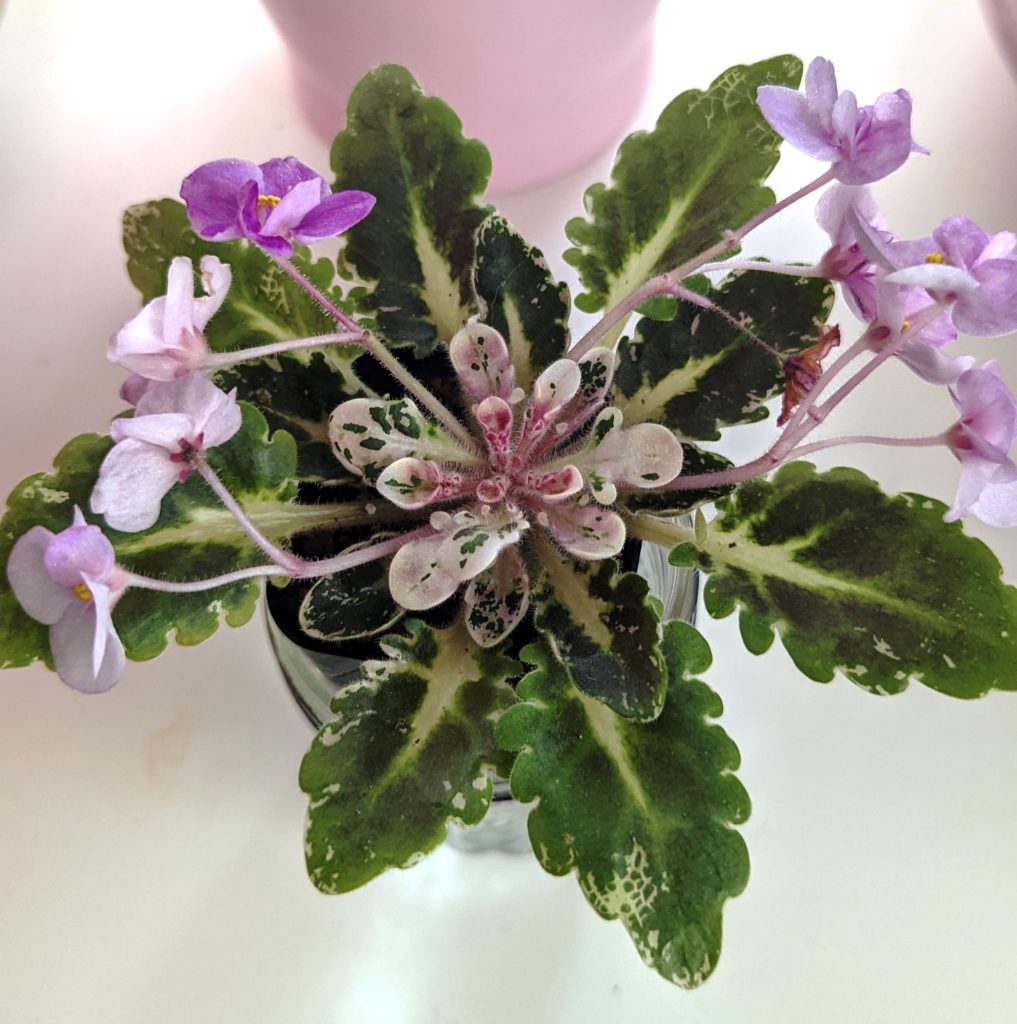




What is edge variegation in African violets?
- Edge variegation is a type of leaf variegation seen in African violets (Saintpaulia) where the margins or edges of the leaves are a different color from the rest of the leaf.
- This can range from white, yellow, or pink hues. The specific pattern can vary depending on the cultivar and the extent of the variegation can also vary, from a narrow border to a wide band.
- Edge variegation is a highly desirable ornamental feature in African violets and many cultivars have been developed specifically to produce this pattern.
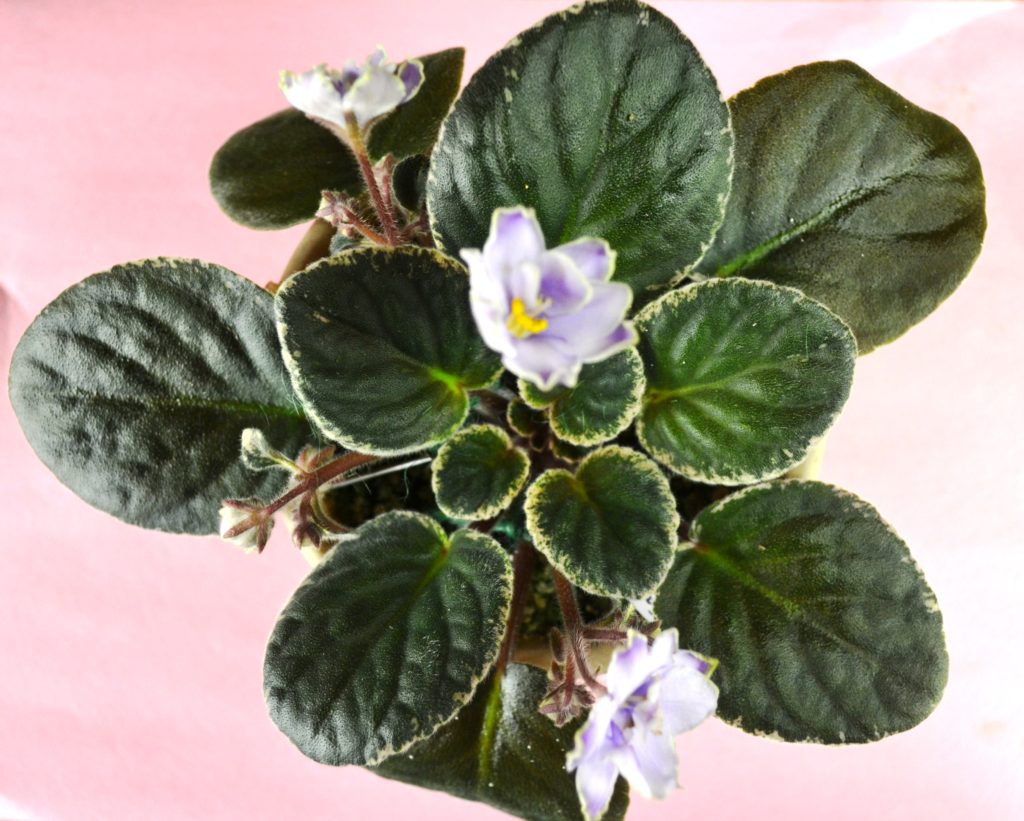
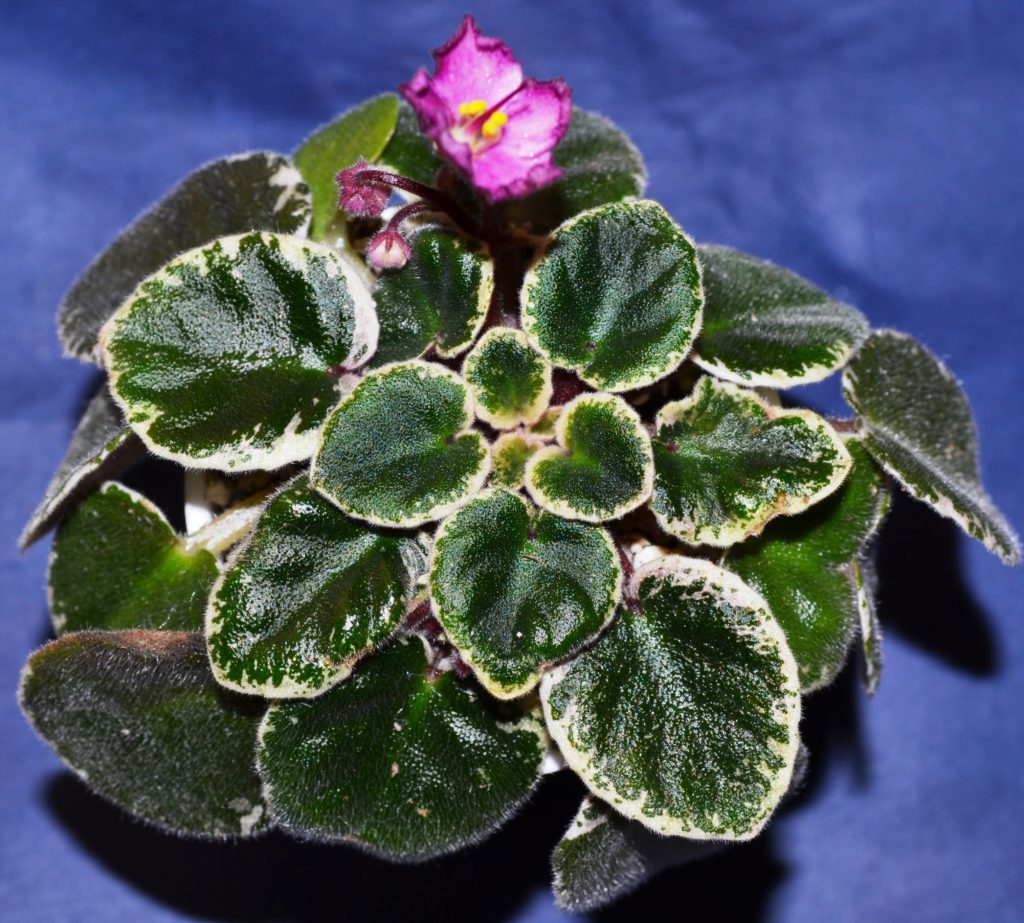
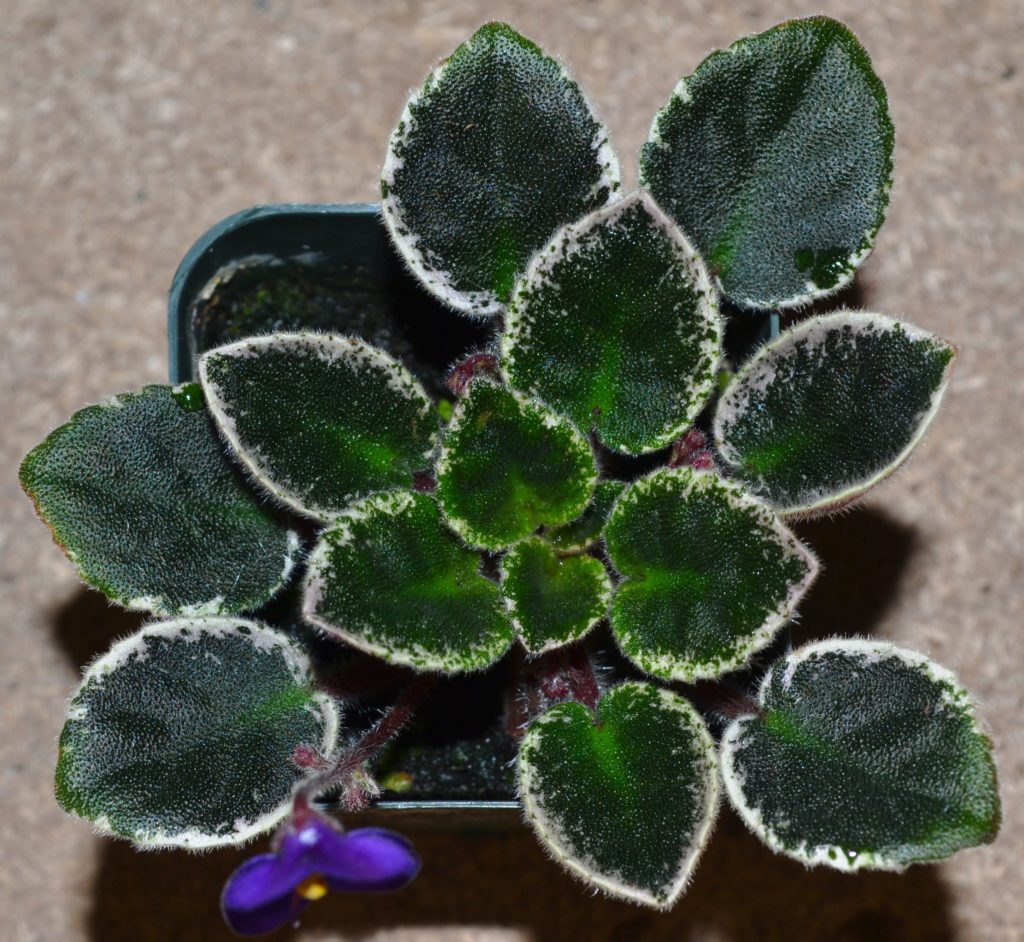
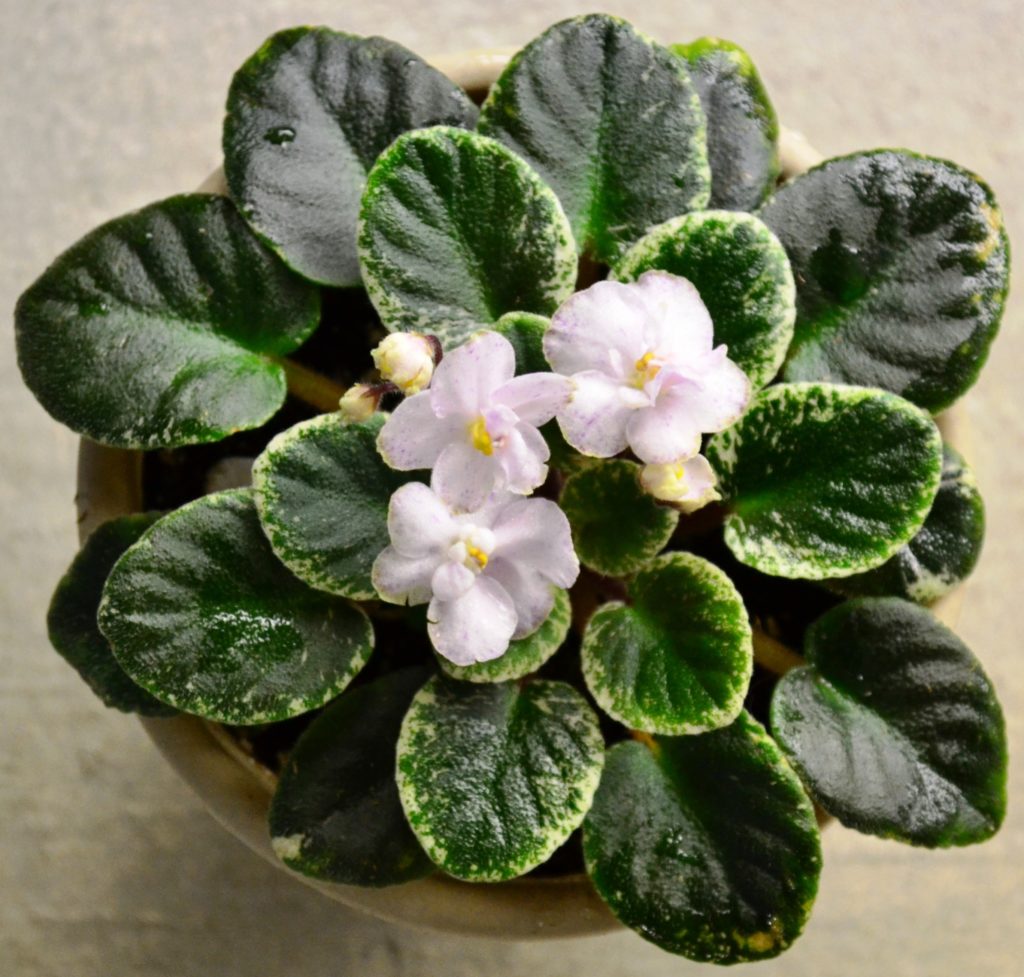




What is crown variegation in African Violets?
- Crown variegation is a type of leaf variegation seen in African violets (Saintpaulia) where the center of the leaf is a different color from the rest of the leaf.
- This can range from white, yellow, or pink hues. The specific pattern can vary depending on the cultivar and the extent of the variegation can also vary, from a small central patch to a large section of the leaf.
- Crown variegation was formerly named as champion variegation.
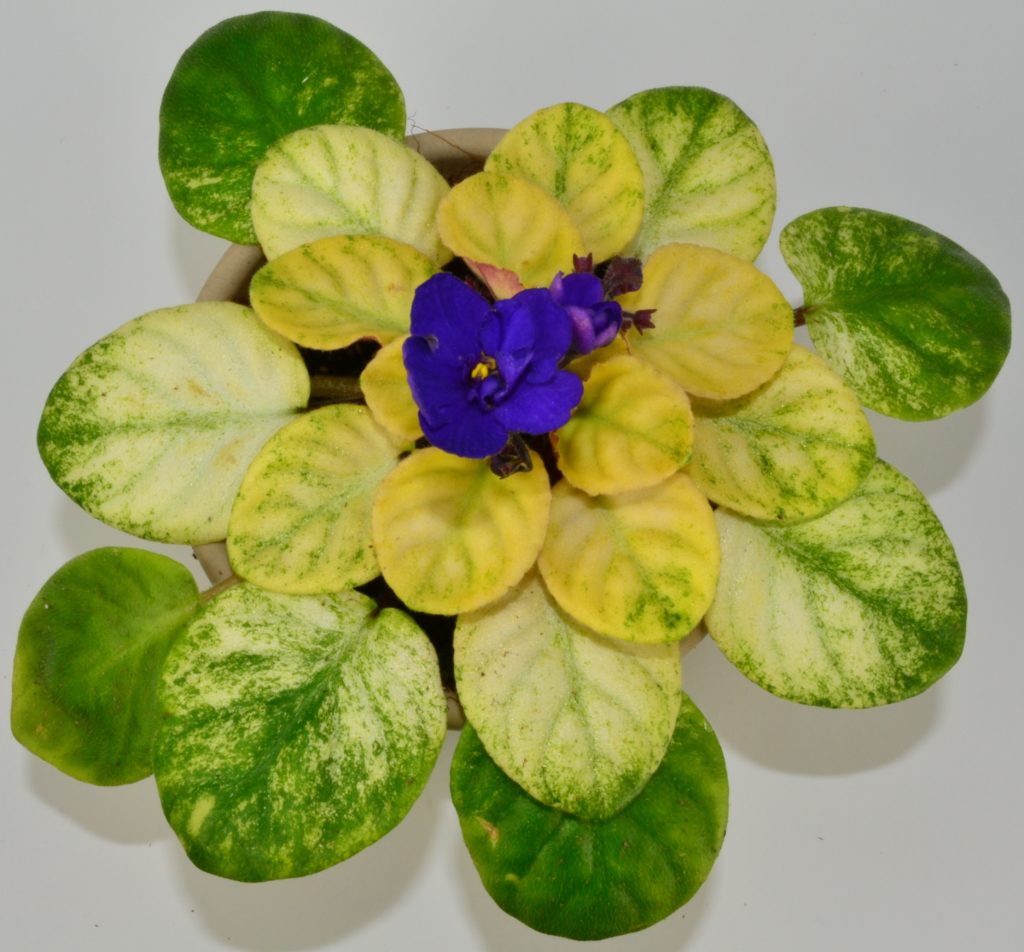
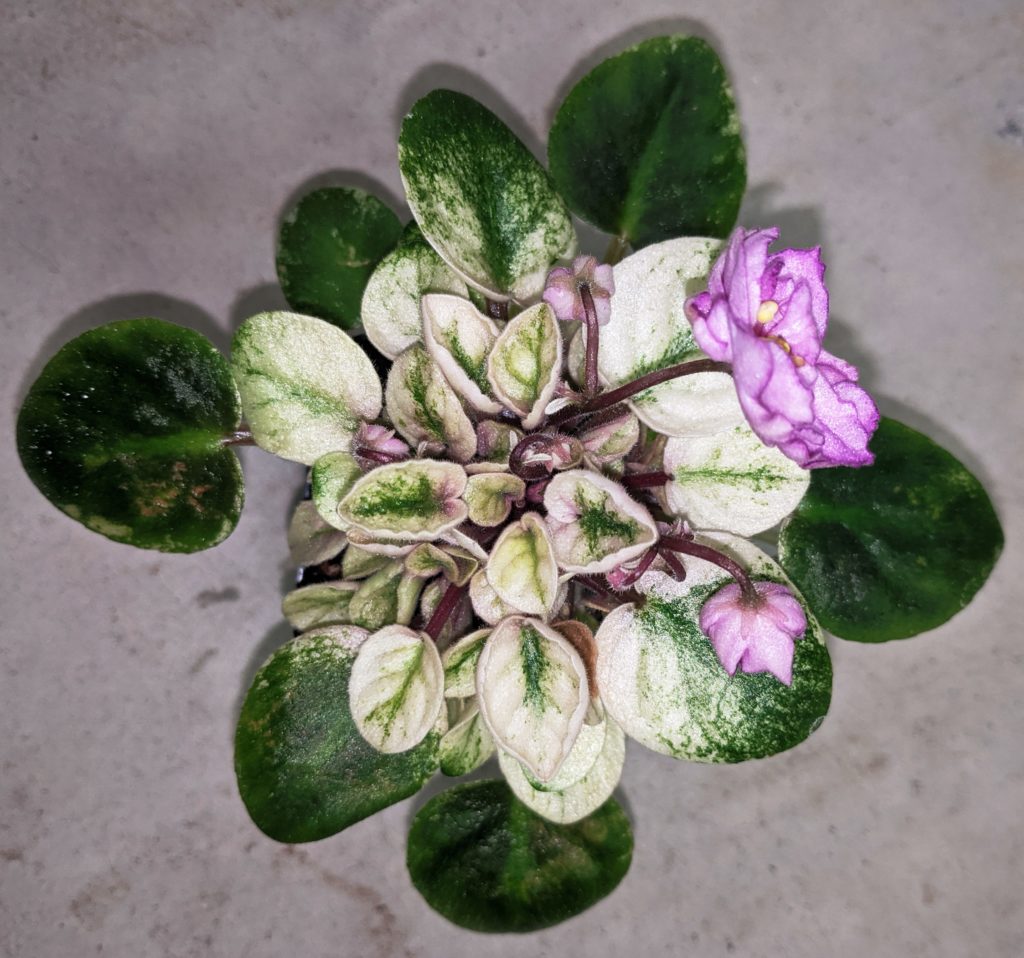
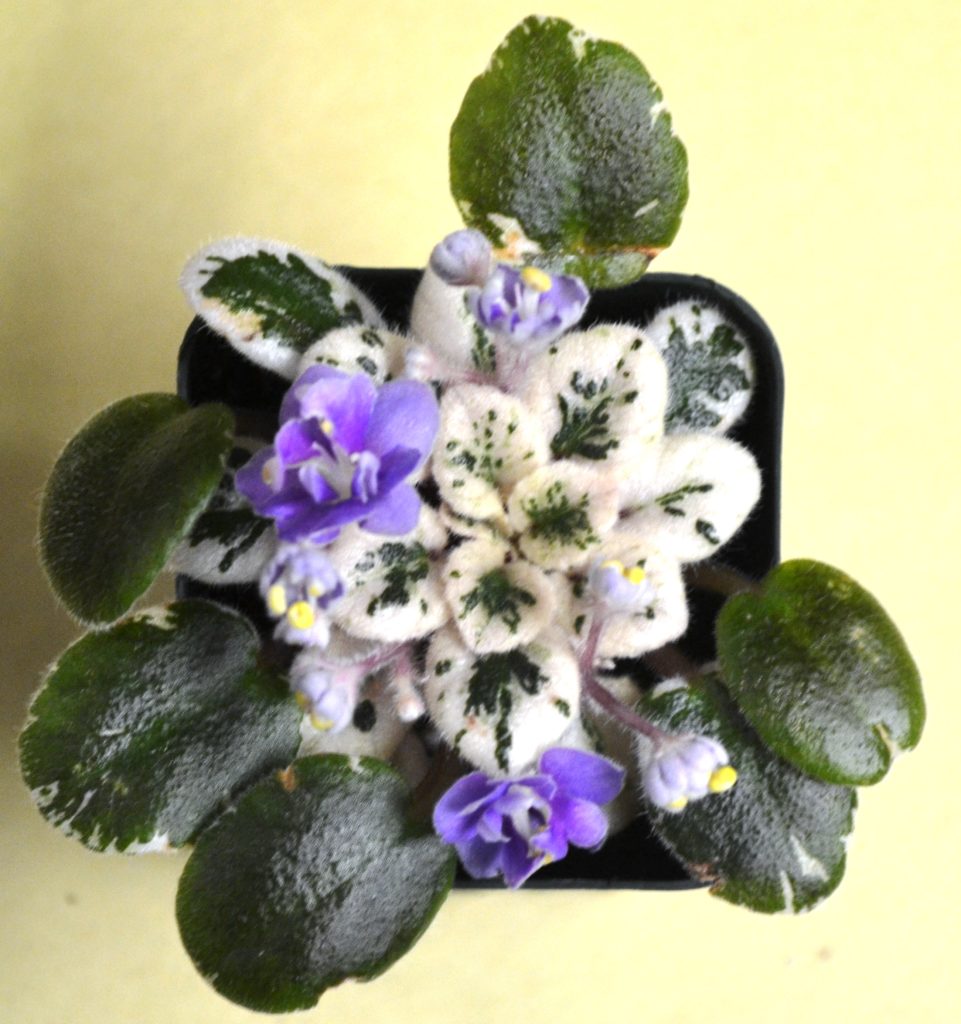
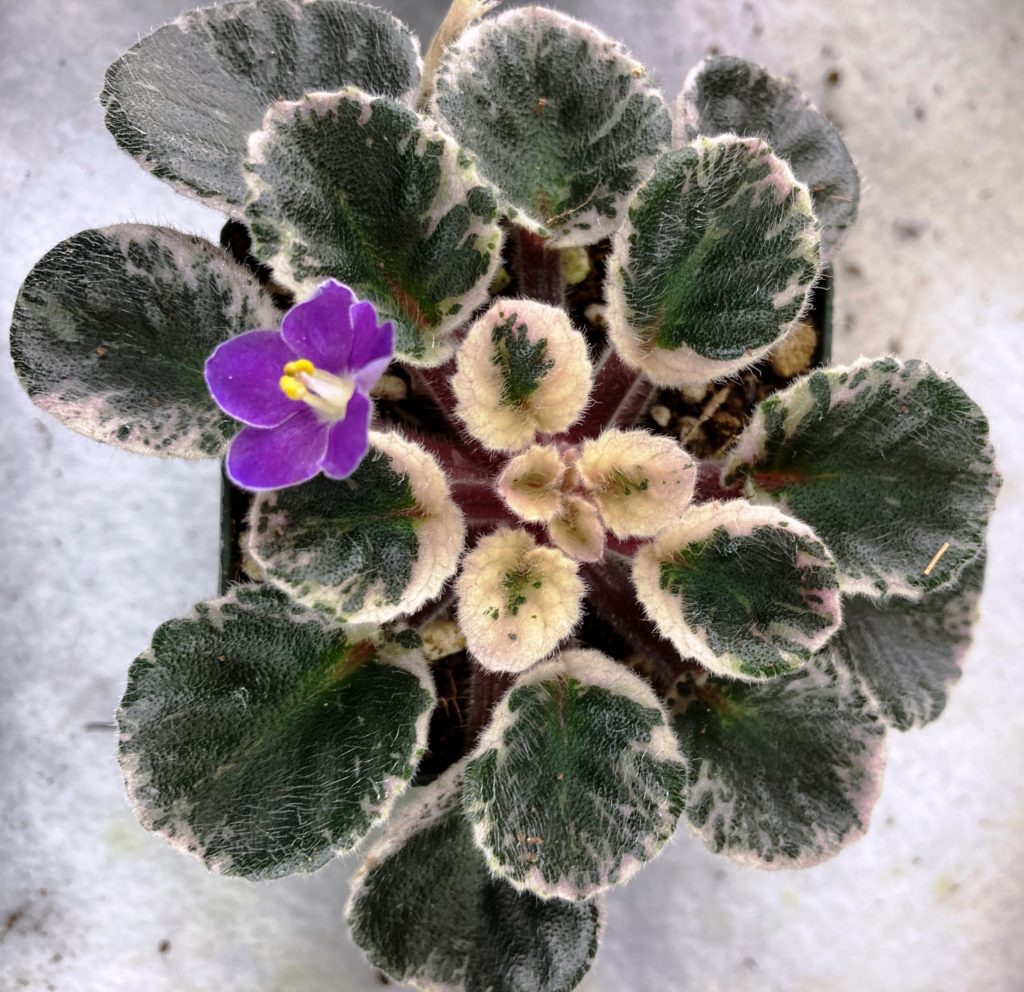




What is mosaic variegation in African Violets?
- Mosaic variegation is a type of leaf variegation seen in African violets (Saintpaulia) where small patches of a different color are scattered across the leaf.
- The patches can range from white, yellow, or pink hues. The specific pattern can vary depending on the cultivar, with some leaves having a few patches while others have many patches scattered throughout.
- Mosaic variegation is a highly desirable ornamental feature in African violets and many cultivars have been developed specifically to produce this pattern.
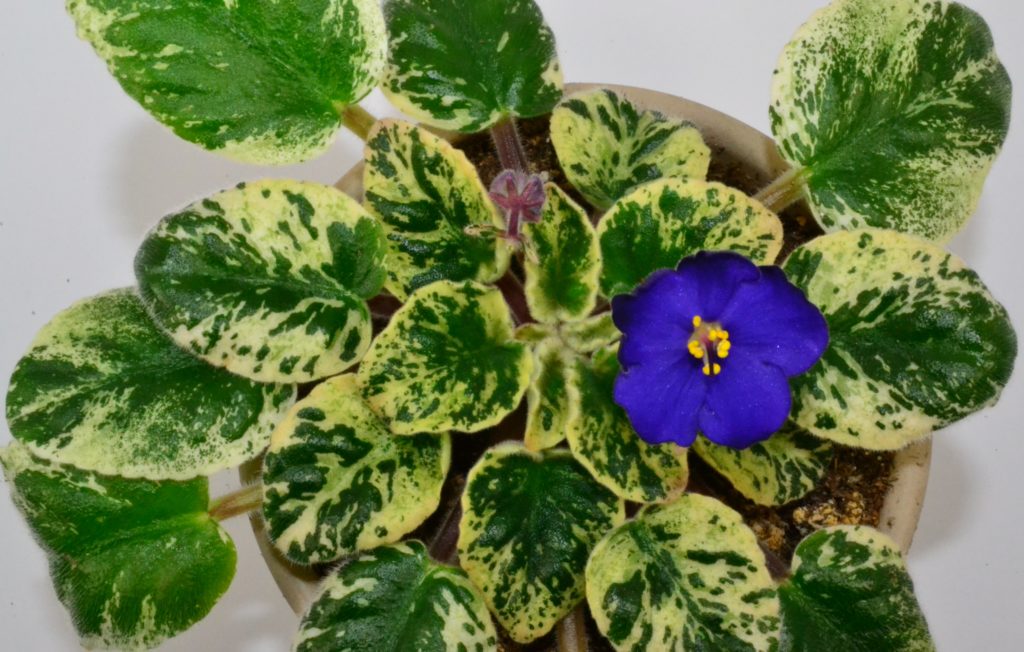
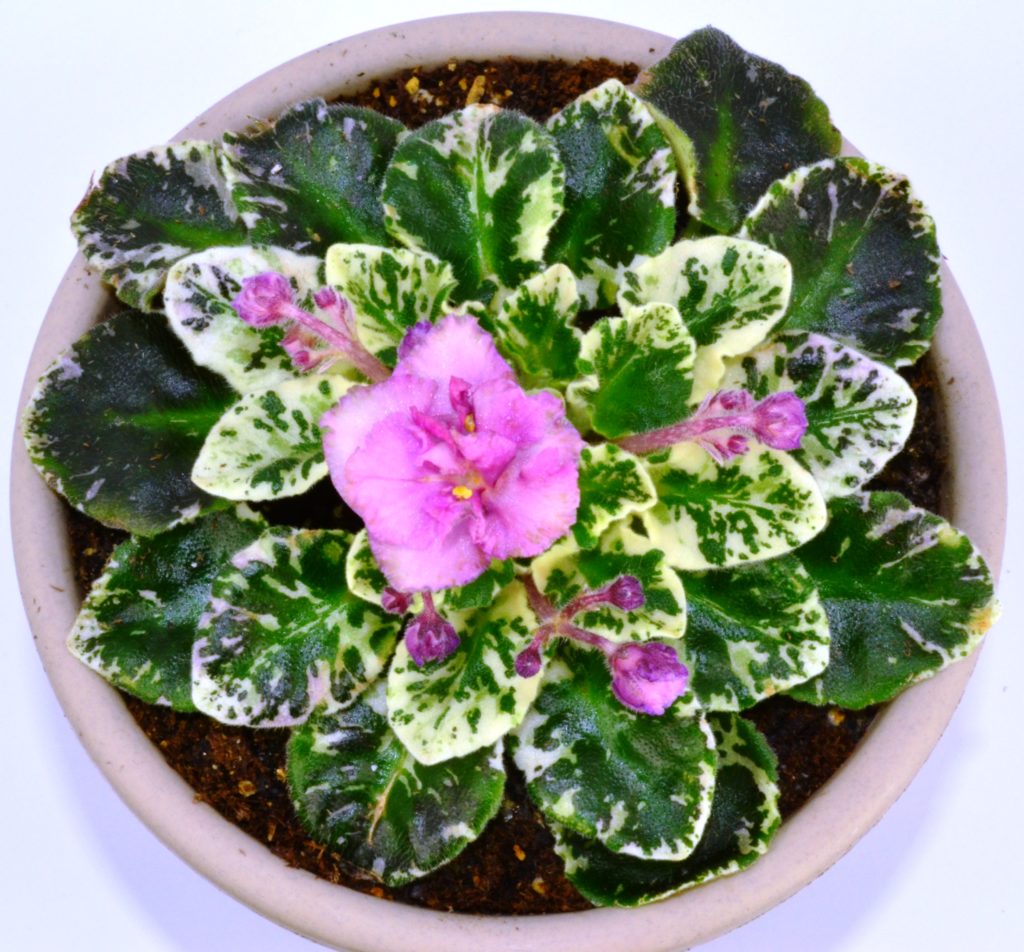
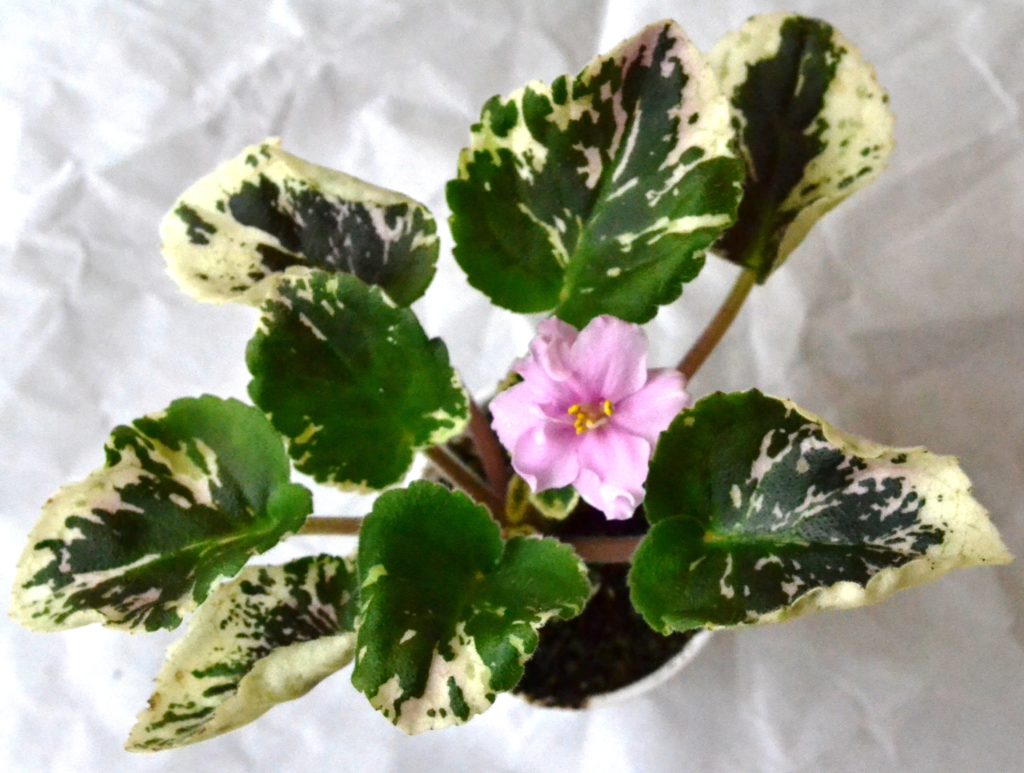
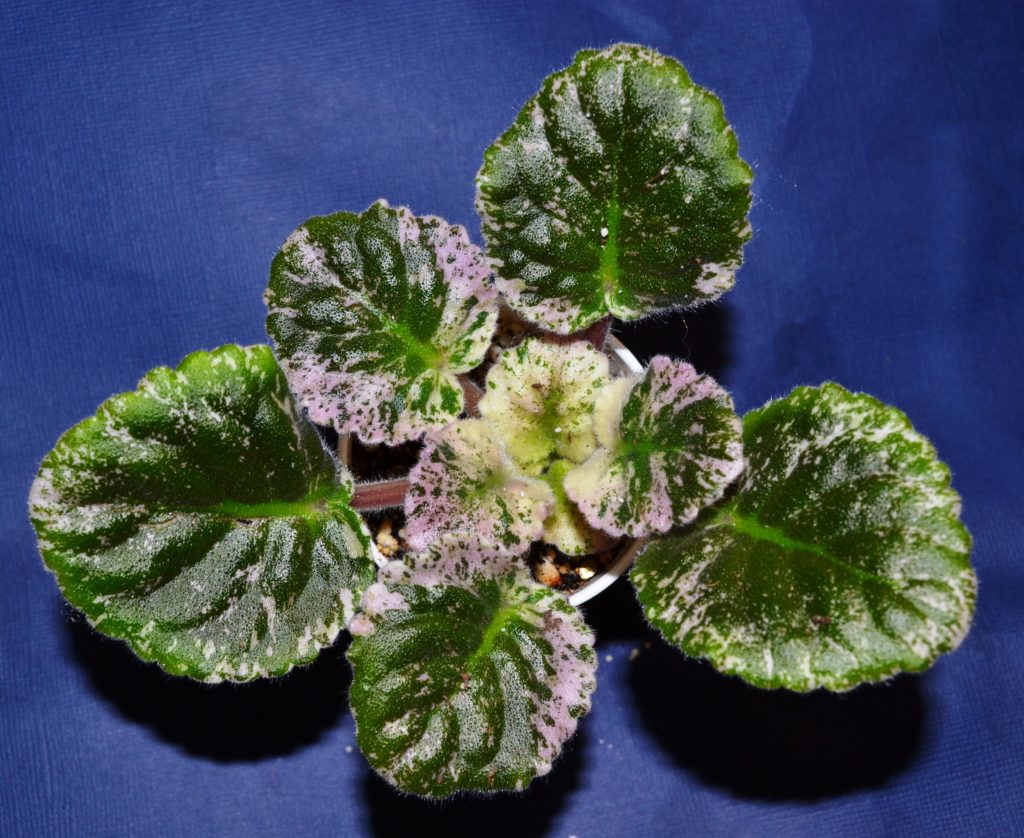




How to fertilize variegated African Violet plants?
- To fertilize variegated African violet plants, you can use a balanced water-soluble fertilizer specifically formulated for African violets, such as a 20-20-20 formula. The recommended application rate is usually around 1/4 to 1/2 teaspoon per gallon of water. It’s important to avoid over-fertilizing, which can cause excessive leaf growth and reduce flowering.
- It’s best not to fertilize variegated African Violets frequently as the variegation will fade over time. Generally you can fertilize once a season, either in spring or fall and that should be enough for them. If you fertilize variegated African Violet plants too frequently, then fertilizer burn can occur (brown spots on the tips / margins of the leaf). Another reason, to not fertilize too much, is that variegated African Violet leaves have less green parts, which means they have less chlorophyll in their leaves and as a result process relatively less food.
Here’s a general guideline for fertilizing variegated African violets:
- Water your African Violet plants thoroughly, allowing the soil to drain well.
- Mix the fertilizer into the water at the recommended rate.
- Apply the fertilizer solution to the soil, making sure to not splash it on the African Violet leaves.
- Allow the soil to dry out slightly between waterings to prevent root rot.
- Repeat the fertilization every 6-8 months, depending on the growing conditions and the health of the African Violet plant.
- It’s also important to monitor the health of your African Violet plants and adjust the fertilization schedule as needed. Overfertilization, underwatering, and overwatering can all cause leaf yellowing or other issues. Proper watering, light, and humidity levels are also important for the overall health and growth of variegated African violets. Can learn more about fertilizing African Violets from this article, Fertilizer for African Violet Plants?
Examples of commercially available African Violet fertilizers below, also my favorite African Violet fertilizer, optimara:
How to take care of variegation African Violet plants?
Growing variegated African violets (Saintpaulia) requires providing them with suitable conditions such as:
- Light: Provide bright, indirect light. Avoid direct sun, which can cause African Violet leaf damage and fade the variegation.
- Temperature: Keep the temperature between 60-70°F (16-21°C) during the day and 50-60°F (10-16°C) at night. Avoid temperature fluctuations and cold drafts near variegated African Violet plants.
- Humidity: African violets prefer a relative humidity of 50-60%. You can increase humidity by placing a tray of water near the plant or using a humidifier.
- Soil: Use a well-draining African violet potting mix or a mixture of equal parts peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite.
- Watering: Water the soil thoroughly and allow it to drain well. Do not allow the plant to sit in water, which can lead to root rot. Water with tepid water when the top inch of soil is dry.
- Fertilizing: Fertilize every 6-8 months with a balanced water-soluble fertilizer specifically formulated for African violets, such as a 20-20-20 formula. Avoid over-fertilizing, which can cause excessive leaf growth, fertilizer burn and reduced flowering.
- Repotting: Repot when the roots fill the pot and the plant becomes pot-bound. Use a slightly larger pot and fresh potting mix.
By following these guidelines, you can help ensure that your variegated African Violets grow healthy and thrive. Regularly monitoring the plants for any signs of stress, such as yellowing leaves or reduced flowering, and making adjustments to the care regimen as needed can also help maintain their health and beauty.
Below are examples of plastic pots of different sizes:
Try to use long thin spout watering cans as shows below, its easier to give water to the potting soil this way.
Why are my variegated African Violet leaves turning green?
Variegated African Violet leaves turning green can happen for several reasons, including:
- Over-fertilization: Excessive fertilizer can lead to excessive African Violet leaf growth and the greening of variegated leaves.
- Lack of light: If the plant is not receiving enough light, the green pigments in the African Violet leaves will become more prominent as the plant tries to photosynthesize more efficiently.
- High humidity: High humidity can cause an increase in chlorophyll production and the greening of variegated African Violet leaves.
- Age: As variegated African Violet leaves age, they may naturally lose their variegation and turn green.
- Genetic reasons: In some cases, the loss of variegation can be due to genetic factors.
To prevent the greening of variegated African Violet leaves, it is important to provide your plant with appropriate light, temperature, humidity, and fertilizer levels, as well as proper watering. If the problem persists, it may be helpful to consult a specialist or take a cutting from the African Violet plant and start a new one to maintain its variegation.
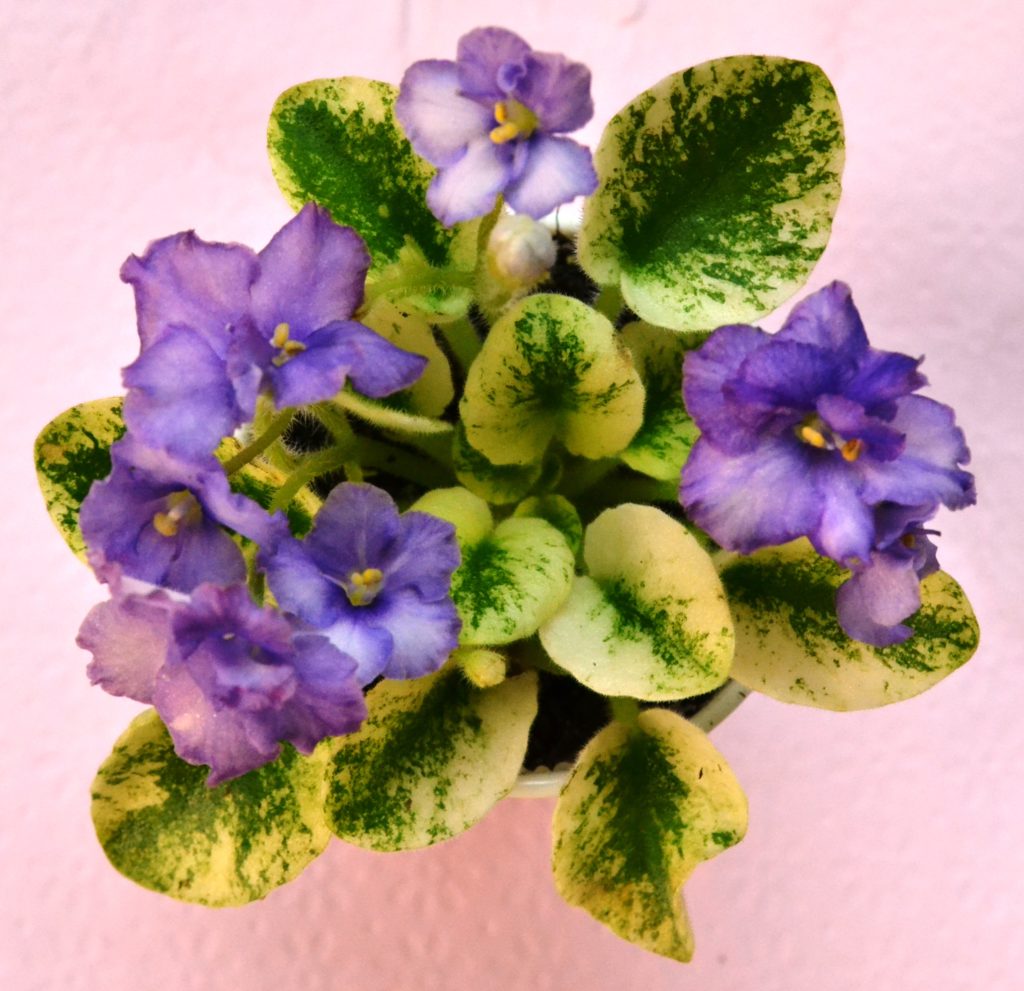
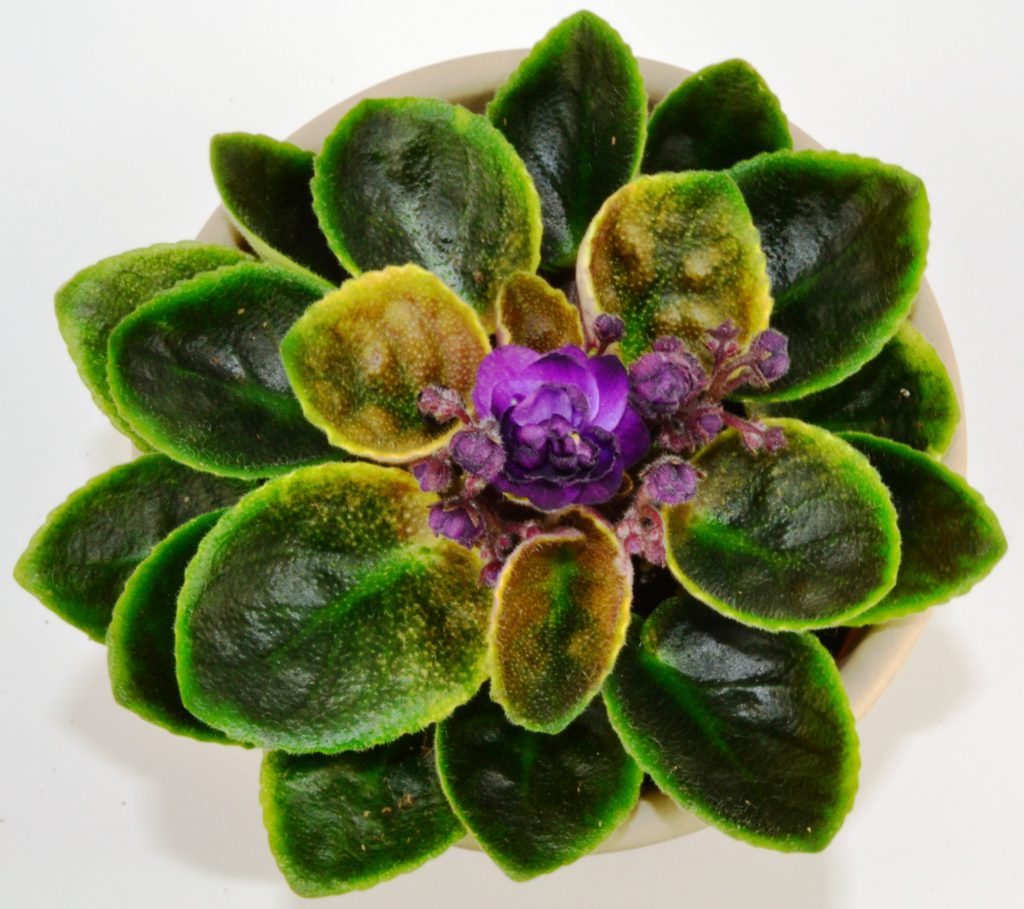
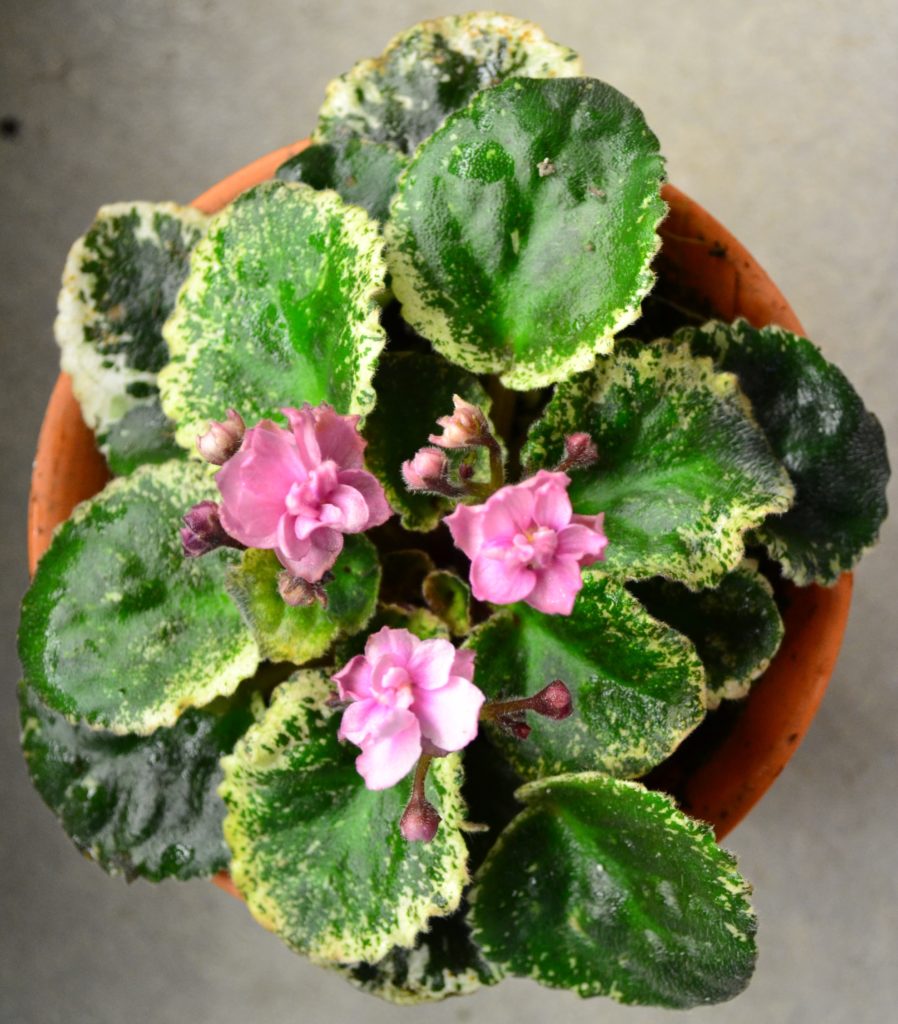
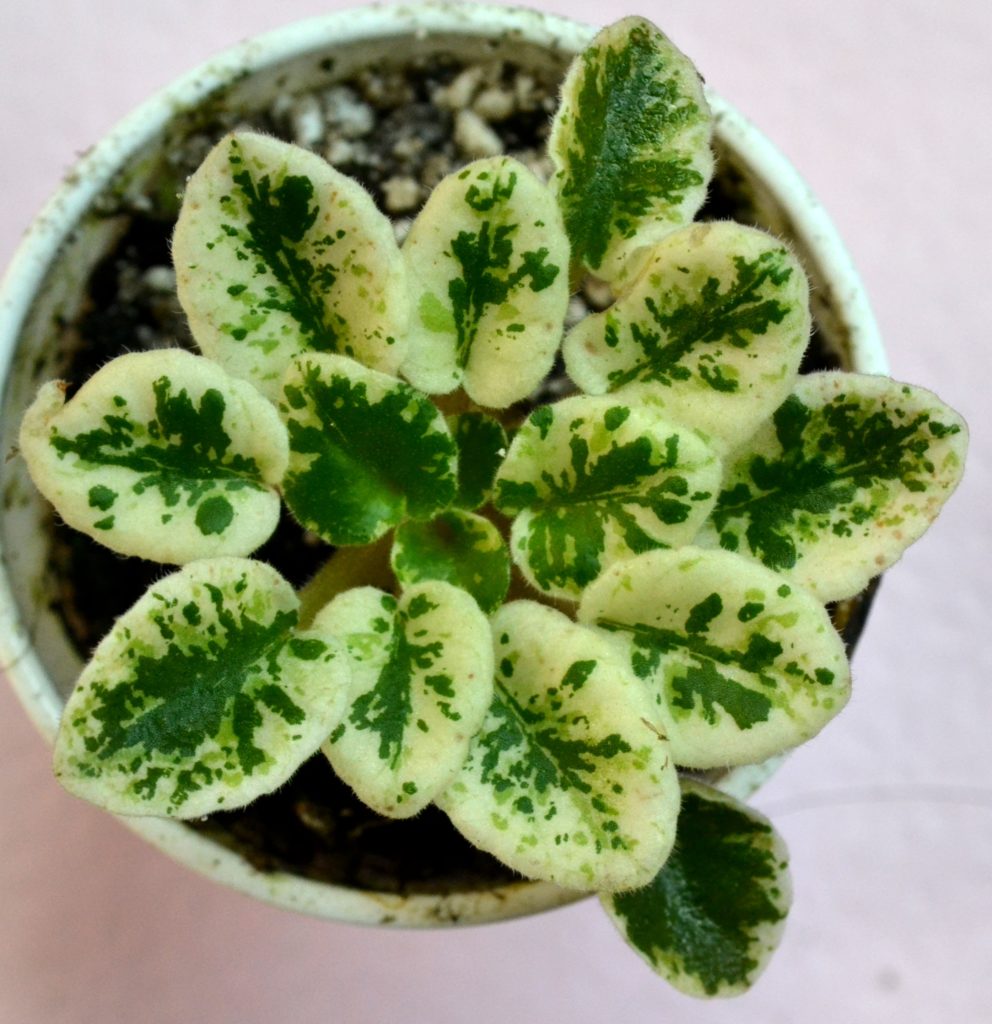




How can I maintain variegation in my African Violet plant leaves?
To maintain variegation in your African Violet plant leaves, you should:
- Provide adequate light: Variegated African Violet plants require bright, indirect light to maintain their color patterns. Avoid exposing them to direct sun, which can cause damage to the leaves and fade the variegation.
- Avoid over-fertilization: Over-fertilizing can cause excessive leaf growth, which can reduce the visibility of the variegation. Fertilize the African Violet plant regularly, but in moderation, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Monitor temperature and humidity: Maintain a consistent temperature and humidity range for your plant. Large fluctuations can stress the African Violet plant and cause the variegation to fade.
- Prune regularly: Pruning regularly can remove older, less variegated leaves and promote the growth of new, more vibrant leaves.
- Use disease-free propagation material: When propagating variegated African Violet plants, use disease-free cuttings to avoid introducing any diseases that could stress the African Violet plant and cause the variegation to fade.
By following these guidelines, you can help maintain the variegation in your plant leaves. Regularly monitoring the plant and making any necessary adjustments to its care regimen can also help ensure that the variegation remains vibrant and visible.
Tool recommendations below, useful in removing suckers or slicing leaves for propagation too.
Why are my African Violet leaves turning white?
African violet leaves turning white can be caused by several factors, including:
- Over-watering: Over-watering can lead to root rot, which can cause the African Violet leaves to turn white as they die.
- Lack of humidity: Low humidity can cause the African Violet leaves to dry out and turn white.
- Sunburn: Direct sunlight can cause the leaves to turn white due to sunburn.
- Disease: Certain diseases, such as powdery mildew, can cause the leaves to turn white.
- Pesticides: Overuse of pesticides or exposure to harsh chemicals can cause the leaves to turn white.
To prevent African Violet leaves from turning white, it’s important to provide the plant with adequate water, humidity, and light, as well as a well-draining soil mix. You should also avoid overuse of pesticides and protect the African Violet plant from direct sun exposure. If you suspect a disease, consult a specialist and follow their recommendations for treatment.
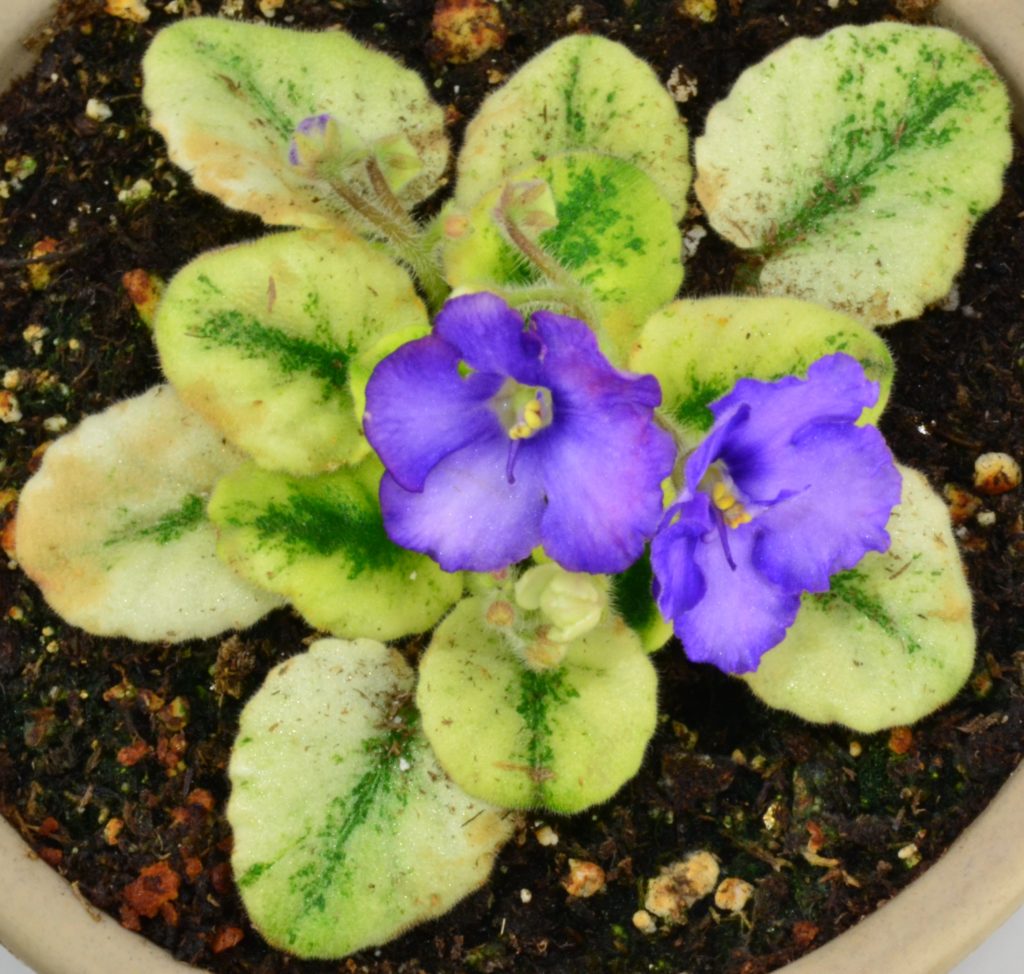
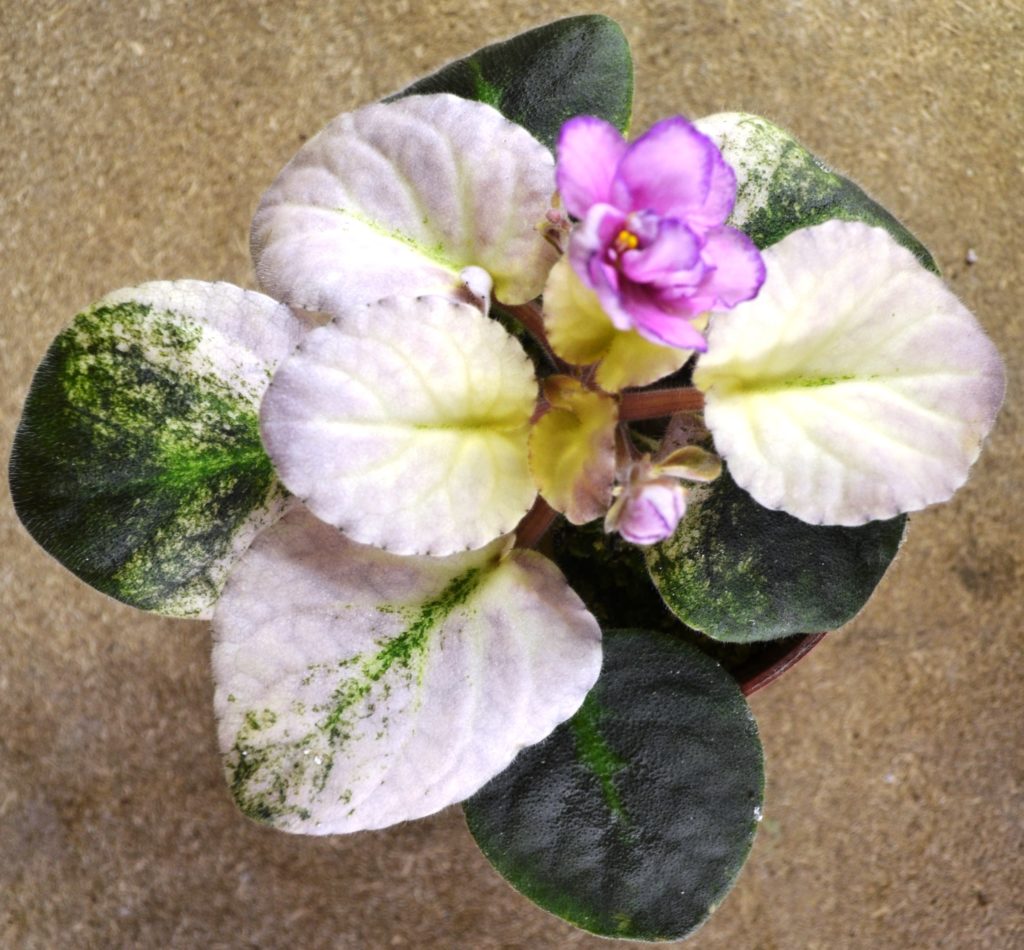
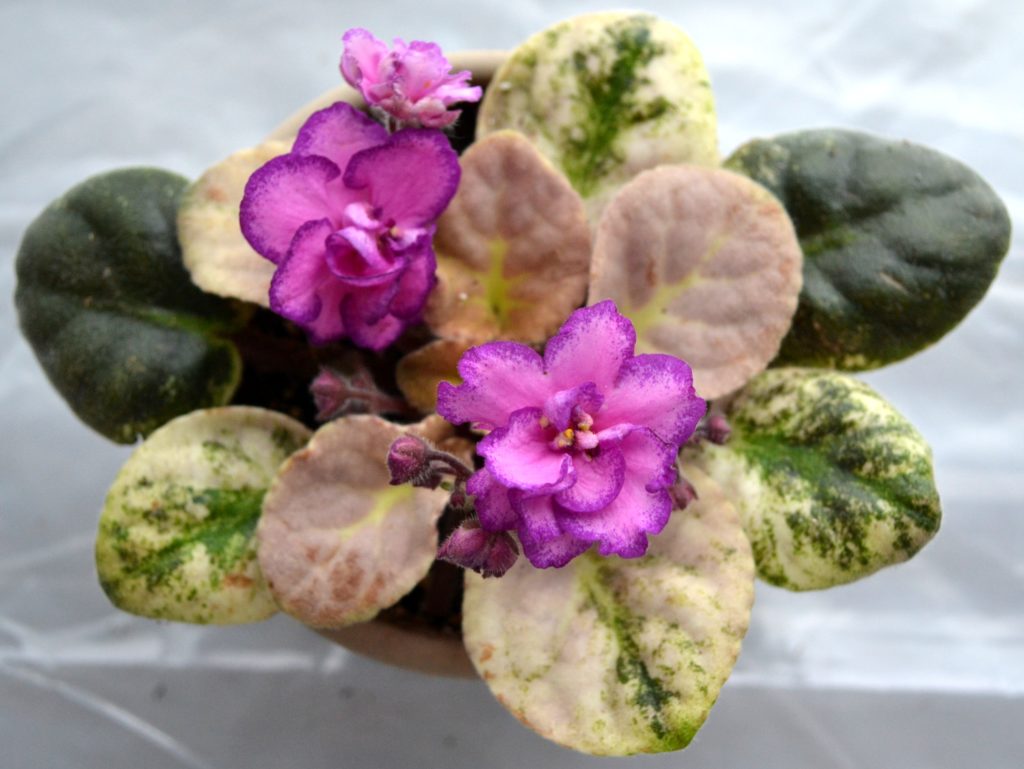
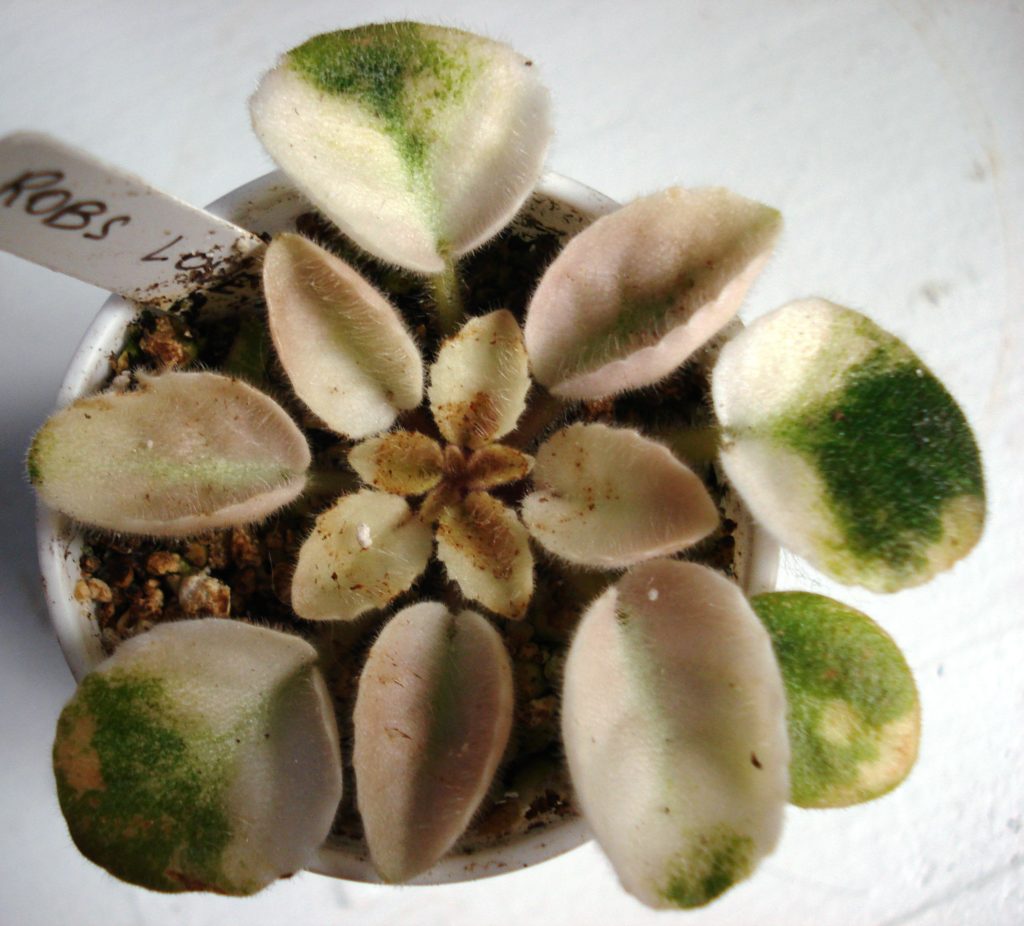




How to take variegated African Violet leaf cuttings for propagation?
- If you decide to propagate your variegated African Violet plant, make sure to select leaves with a higher percentage of green area.
- The new plantlets which will emerge will need lots of energy to grow, which will be provided by the chlorophyll present in the mother leaf.
- You can try to take leaves from plants which have completely cream, white or pink leaves with no green at all, however the chances of survival are less.
To take variegated African Violet leaf cuttings for propagation, follow these steps:
- Choose a healthy leaf: Select a healthy, mature leaf from the parent African Violet plant with a visible stem (petiole).
- Cut the leaf: Using a sharp, clean pair of scissors, cut the leaf from the parent African Violet plant just below the petiole.
- Prepare the cutting: Remove any lower leaves from the cutting so that only the top half of the leaf remains.
- Propagate: There are several methods for propagating African violet leaf cuttings, including rooting in water or soil, or planting directly into soil.
- Water and care: Keep the cutting moist and in bright, indirect light until it has rooted and begun to grow.
It is important to note that not all variegated African Violet plants will produce variegated offspring from leaf cuttings. This can depend on the specific genetics of the plant and the method of propagation used. However, by carefully selecting healthy leaves and providing proper care, you can increase your chances of successfully propagating variegated African violets from leaf cuttings. Can learn more about propagating African Violets from this article, African Violet Leaf Propagation: How to Produce Baby Plantlets?
Below are examples of pruning / grooming tools for African Violet plants:
How does temperature affect variegation in African Violet plants?
- Temperature can have a significant impact on the variegation in African Violet plants. Sudden changes in temperature, either increases or decreases, can stress the plant and cause the variegation to fade or disappear altogether.
- Consistent fluctuations in temperature can also cause stress and reduce the visibility of the variegation.
- African violets prefer a consistent temperature range of 65-75°F (18-24°C). Exposure to temperatures outside of this range, especially for extended periods of time, can cause stress and affect the variegation.
- To maintain the best variegation, it’s important to provide the plant with a stable, consistent temperature and avoid exposing it to sudden temperature changes.
- Additionally, temperature can also affect the rate of growth and overall health of the plant, which can also impact the variegation.
- By providing the plant with the ideal temperature range and avoiding temperature fluctuations, you can help ensure that the variegation remains vibrant and visible.
Below are examples of temperature and humidity meters, useful to keep in your growing area, especially when monitoring powdery mildew on your plants.
How does light affect variegation in African Violet plants?
Light is a crucial factor in maintaining the variegation in African Violet plants. The amount and quality of light can directly impact the visibility and intensity of the variegation.
- African violets prefer bright, indirect light and will grow best in a location that receives filtered sunlight for a few hours each day.
- Direct sunlight can cause the leaves to sunburn and the variegation to fade, so it’s important to provide shade during the hottest hours of the day. Additionally, insufficient light can cause the plant to stretch and the variegation to become less visible.
- If an African Violet plant has a lot of variegation, it will need less light. If it is exposed to bright light, the leaves will get scorched. Its best to keep heavily variegated plants away from the direct sunlight.
- If the variegated African Violets are being grown under fluorescent tubes, its best to keep these plants at the ends of the tubes where the light is much cooler as compared to the center area of the tubes.
- For LED lights it does not matter, as the temperature is evenly distributed along the lights.
- By providing the plant with the appropriate amount of bright, indirect light, you can help maintain the intensity and visibility of the variegation in African Violet plants. Additionally, rotating the plant regularly can help ensure that it receives even light exposure and can prevent one-sided growth.
Conclusion:
- African Violet variegation is quite sensitive and can be temperamental. Sometimes the variegation trait can be lost when an African Violet plant is propagated using leaves.
- Sometimes the variegation trail can be lost due to external environmental condition. It can also happen, that in the summer months, the variegated African Violet plants plants will be heavily green in color due to the warmer temperatures.
- As the weather cools down in the winter, the variegation trait will be back in the same African Violet plant. T
- Even, variations in light or fertilizer may also cause a variegated African Violet plant to revert back to its green leaves from its variegated leaf trait, especially if the light and fertilizer and higher than normal.
- But do not worry, even if a plant changes to green leaves, over time a the favorable conditions return back, the variegation pattern also returns back.
Examples of self watering pots for African Violet plants as shown below:

*Our Affiliate Programs: We are a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for us to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.
Though we do link to many items on Amazon out of convenience to our readers, we do also participate in other affiliate programs that also pay us a commission for any purchases you might make through our links (at no additional cost to you!).